A successful marketing plan needs proper segmentation, targeting, and positioning. The process of segmentation, targeting, and positioning is called STP Model ((segmentation, targeting, and positioning).
For a brand and its products to be successful, the marketer needs the identify the segments of the market and understand under which bases each segment falls. Once the segments are identified, targeting’s job is to find suitable ones for the brand that has the potential for high sales numbers, growth, and low competition. Lastly, marketing positioning takes over. Its job is to develop a marketing mix that puts the product in a unique position to the targeted segments for attracting potential buyers.
In this post, we will understand the 3 steps of the STP Model(segmentation, targeting, and positioning)
3 Steps of Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning (STP) Model
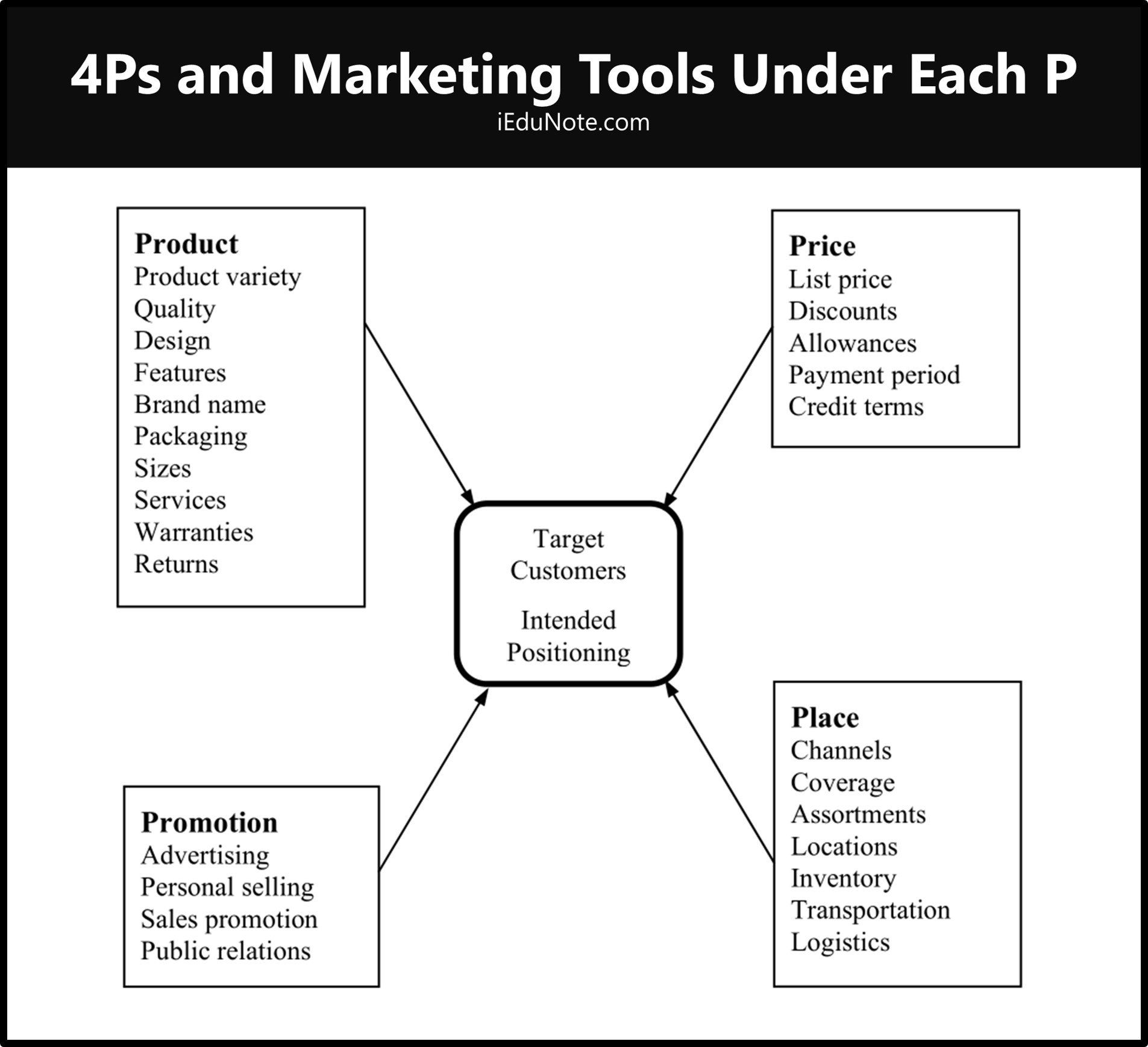
No brand or company can satisfy all customers, so it is up to the company to select the specific parts of the market, which they can best serve.
So, businesses could identify market segments, select a few profitable segments, and develop products and marketing mixes aimed at particular customers.
Target marketing is made up of 3 stages;
- market segmentation,
- marketing targeting, and
- product positioning.
Students need to get clear; ‘marketing targeting’ and ”target marketing’ sound similar but are different.
‘Marketing targeting’ is the 2nd step of ‘target marketing,’ where marketers evaluate and select the best segments in the market.
Market segmentation is the identification of customer groups who share similar characteristics. This process has several advantages and enables a marketing manager to design an effective plan for each segment.
Usually, tourism companies segment their market by using demographic, geographic, psychographic, behavioral, and product-related variables. The chosen segments ought to be measurable, accessible, substantial, and actionable.
Therefore, proper target marketing is necessary for the best market coverage plan.
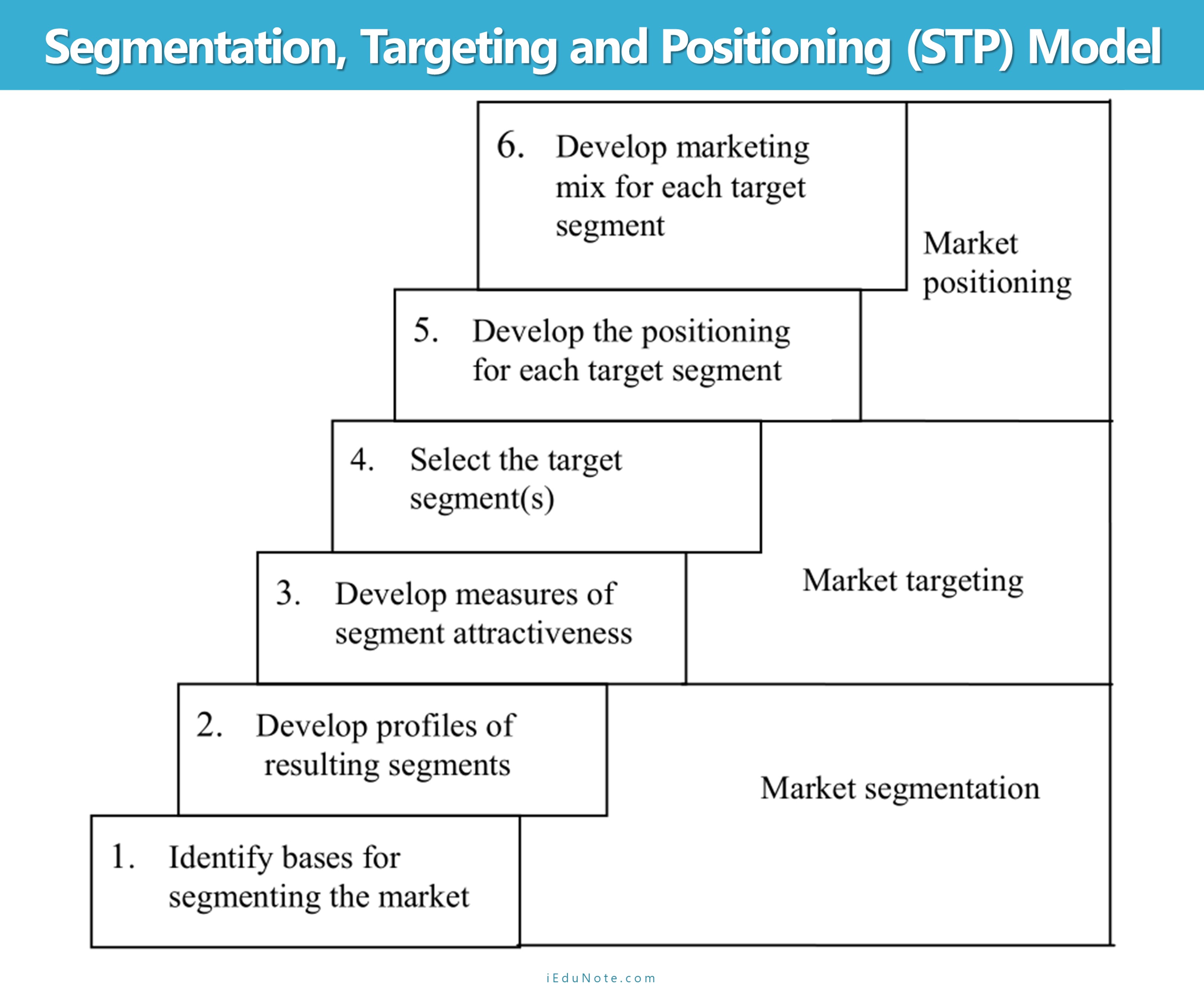
All three stages of target marketing have two important tasks these are;
- Market Segmentation
- Identify the bases for segmenting the market.
- Develop profiles of resulting segments
- Market Targeting
- Develop measures of segment attractiveness
- Select the target segment(s)
- Marketing Positioning
- Develop the positioning for each target segment
- Develop a marketing mix for each target segment
Let’s try to understand them.
A. Market Segmentation
The first is market segmentation, dividing a market into smaller groups of buyers with distinct needs, characteristics, or behaviors who might require separate products or marketing mixes. The company identifies different ways to segment the market and develops profiles of the resulting market segments.
Segmenting strategies include demographics, lifestyle, geographic and behavioral approaches. Demographics segmentation means you break up markets based on personal traits like age, race, marital status, gender, and income. Lifestyle segmenting means you divide customers by hobbies and interests.
Geographic segmentation makes the local, state, regional, national, or international markets key. Behavioral segmenting is based on such things as usage patterns and benefits sought from the product.
-
Identify the bases for segmenting the market.
A brand needs to select the bases properly for the market segmentation. Depending on the market type, the bases or types of market segmentation will vary.
For the consumer market, the bases of segmentation are;
- Geographic Market Segmentation
- Demographic Market Segmentation
- Psychographic Market Segmentation
- Behavioral Market Segmentation.
For segmentation of the business market, the bases are
- Demographics
- Operating Variables
- Purchasing Approaches
- Situational Factors
- Personal Characteristics
-
Develop profiles of resulting segments
From the bases, the market segmentation process develops a profile of a suitable group of customers or buyers that will provide the most sales. This segment(s) needs to be measurable, actionable and has growth potential.
B. Market Targeting
The second step is market targeting—evaluating each market segment’s attractiveness and selecting one or more of the market segments to enter. In evaluating different market segments, a firm must look at 3 factors:
- Segment size and growth: Analyze current segment sales, growth rates, and expected profitability.
- Segment structural attractiveness: Level of competition, Substitute products, Power of buyers, and Powerful suppliers.
- Company objectives and resources: Examine company skills & resources needed to succeed in that segment. Offer superior value & gain advantages over competitors.
After evaluating different segments, the company must now decide which and how many segments it will target. The target market consists of buyers sharing common needs or characteristics that the company decides to serve.
-
Develop measures of segment attractiveness
Brands must measure what makes segments attractive to target. This could be the potential sales numbers, lack of competition, number of buyers, growth opportunity.
-
Select the target segment(s)
Based on the product or service type, brands need to select one or more segments to target that will ensure most sales and help the company to grow.
C. Marketing Positioning
The third step is market positioning. Beyond deciding which segments of the market it will target, the company must decide what positions it wants to occupy in those segments.
-
Develop the positioning for each target segment
For all selected target segments, a brand needs to define itself by the attributes that consumers care about. A product’s position is the way the product is defined by consumers on important attributes. Again we can say that the place the product occupies in consumers’ minds relative to competing products.
-
Develop a marketing mix for each target segment
Positioning involves implanting the brand’s unique benefits and differentiation in customers’ minds and setting the brand’s marketing mix in a way that attracts customers more than the competition.