Operating Costing is a method of ascertaining the costs of providing or operating a service. This costing method is applied by undertakings that provide services rather than the production of goods.
Such undertakings, for example, are; transport concerns, gas agencies; electricity suppliers; hospitals; theatres, etc.
Because of the varied nature of activities carried out by the service undertakings, the cost system used is different from that followed in manufacturing concerns.
Industries that are suitable or applicable for operating costing are;
- Transport service: Bus, taxi, truck, railways, etc.
- Welfare services: Canteens, hospitals, libraries.
- Utility suppliers: Gas, Electricity, water.
- Municipal services: Street lighting, road maintenance.
Classification of Operating Cost
The operating costs can be classified into three categories. For example, in the case of a transport undertaking, these three categories are as follows:
- Operating and running charges – These include expenses of variable nature. For example:
- expenses on petrol, diesel.
- Lubricating oil, grease, etc.
- Wages of the driver, conductor, etc. (If payment is based on time or distance of trips).
- The commission is taking on the bridge (Toll).
- Depreciation (If allocated based on mileage run and treated as variable expenses).
- Maintenance charges – These expenses are semi-variable and include the cost of:
- tires and tubes,
- repairs and maintenance,
- spares and accessories, overhaul, etc.
- Fixed or standing charges – These costs are fixed in nature though the operation is on standing position, which includes:
- garage rent,
- insurance,
- road license,
- depreciation,
- interest on capital,
- administrative overheads
- motor vehicle tax
- garage rent
- general supervision
- salary of an operating manager, supervisor, etc.
In the case of transport costing, the following formulas are applicable:
- Run Kilometers = (No. of vehicle x Distance x NO. of Trips x Working Days)
- Passenger Kilometers = (No. of vehicle x Distance x NO. of Trips x Working Days x Actual Passenger Carried)
- Ton Kilometers = (No. of vehicle x Distance x NO. of Trips x Working Days x Goods Carried)
Unit Cost Under Operating Costing
| Service Name | Cost Unit |
|---|---|
| 1. Passenger-transport service | Passenger kilometer |
| 2. Goods transport service | Ton kilometer |
| 3. Electricity supply | Kilowatt-hour |
| 4. Canteen service | Man-meal |
| 5. Hospital | Per patient bed per day |
| 6. Educational institution | Per student |
| 7. Private transport | Running g hour, trip, kilometer |
Distinguish between Operating Costing and Operation Costing.
Operating Costing
It is a method of costing applied by undertakings that provide service rather than the production of commodities. Like unit costing and process costing, operating costing is thus a form of operation costing.
The emphasis under operating costing is on the ascertainment of the cost of rendering services rather than on the cost of manufacturing a product.
Transport companies, gas, and waterworks, electricity supply companies, canteens, hospitals, theatres, schools, etc apply it.
Within an organization, certain departments are known as service departments that provide ancillary services to the production departments.
For example, the maintenance department; powerhouse; boiler house; canteen; hospital; internal transport.
Operation Costing
It represents a refinement of process costing. In this, each operation instead of each process of the stage of production is separately costed. This may offer better scope for control.
At the end of each operation, the unit operation cost may be computed by dividing the total operation cost by the total output.
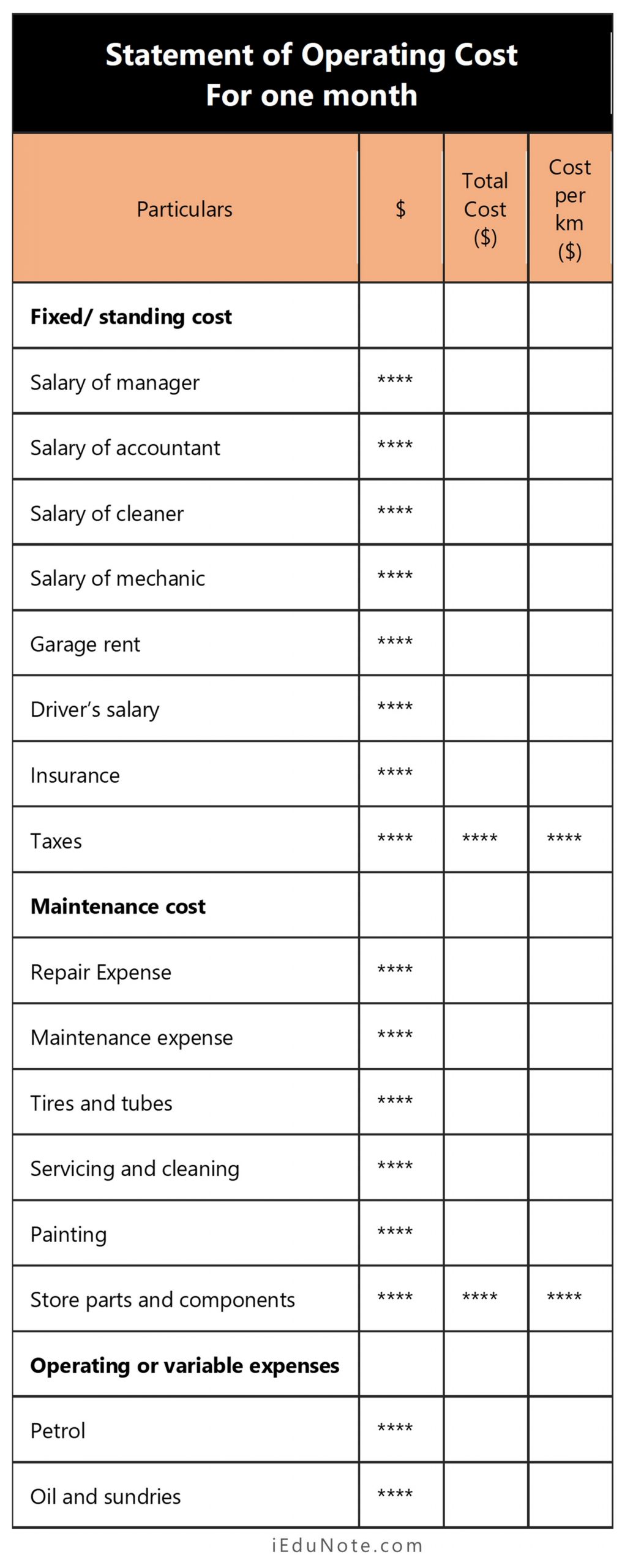
Format of Statement of Operating Cost
Statement of Operating Cost
For one month
| Particulars | $ | Total Cost ($) | Cost per km ($) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed/ standing cost | |||
| Salary of manager | **** | ||
| Salary of accountant | **** | ||
| Salary of cleaner | **** | ||
| Salary of mechanic | **** | ||
| Garage rent | **** | ||
| Driver’s salary | **** | ||
| Insurance | **** | ||
| Taxes | **** | **** | **** |
| Maintenance cost | |||
| Repair Expense | **** | ||
| Maintenance expense | **** | ||
| Tires and tubes | **** | ||
| Servicing and cleaning | **** | ||
| Painting | **** | ||
| Store parts and components | **** | **** | **** |
| Operating or variable expenses | |||
| Petrol | **** | ||
| Oil and sundries | **** | ||
| Lubricating oil | **** | ||
| Grease | **** | ||
| Depreciation | **** | ||
| Cost per ton-km | **** | **** | |
| **** | **** |