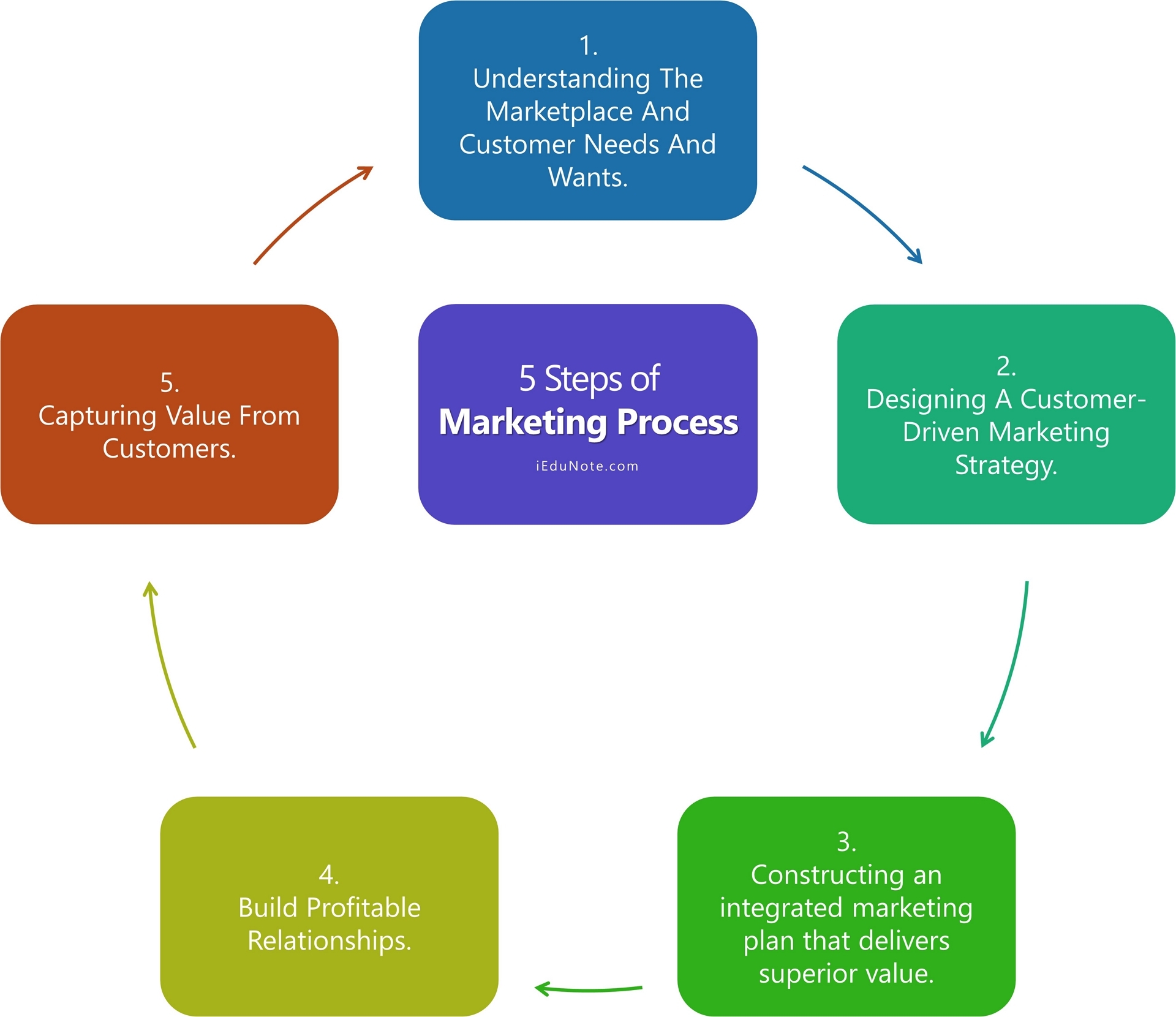
Marketing is how companies create value for customers and build strong customer relationships to capture value from customers in return. The 5-step process of the marketing framework wherein the value is created for customers and marketers capture value from customers in return.
- Understanding The Marketplace And Customer Needs And Wants.
- Designing A Customer-Driven Marketing Strategy.
- Constructing an integrated marketing plan that delivers superior value.
- Build Profitable Relationships.
- Capturing Value From Customers.
Step 1: Understanding The Marketplace And Customer Needs And Wants
It is important to understand customer needs, wants, and demands to build want- satisfying market offerings and building value-laden customer relationships. This increases long-term customer equity for the firm.
Needs – States of felt deprivation
They include the physical need for necessities like food, clothing, shelter, warmth, safety, and individual needs for knowledge and self-expression. The marketers cannot create these needs as they are a basic part of human markup.
Wants – The forms of human needs take as shaped by culture and individual personality.
Wants are shaped by one’s society and are described in terms of objects that will satisfy needs.
For example, an American in Dhaka needs food but wants McDonald’s.
Demands – Human wants that are backed by buying power.
Given their wants and resources, people demand products with benefits that add to the most value and satisfaction.
Step 2: Designing A Customer-Driven Marketing Strategy
Focus areas for designing a marketing strategy:
- Selecting customers to serve -defining the target market
- Deciding how to serve customers in the best way – choosing a value proposition
Selecting customers to serve:
The company first decides who it will serve and divides the market into segments of the customer. Then it goes after specific sections of the market or its target market.
They target customers based on their level, timing, and nature of demand.
Choosing a value proposition
They decide how it will serve their customer. That is how it will differentiate and position itself in the market. A brand’s value proposition is the set of values and benefits that it promises to deliver its customers.
Companies need to design strong value propositions to give them the greatest advantage in their target markets.
5 alternative concepts for designing a customer-driven marketing strategy are;
- Production concept: Consumers will favor products that are available and highly affordable. Management should focus on improving production and distribution efficiency.
- Product concept: Consumers will favor products that offer the most quality, performance, and innovative features. Focus on making continuous product improvements.
- Selling concept: Consumers will not buy enough of the firm’s products unless it undertakes a large-scale selling and promotion effort. It is typically practiced with unsought goods that the company needs to sell and generally results in aggressive selling practices. The company sells what it makes rather than what the market wants.
- Marketing concept: Organizational goals are achieved by knowing the target markets’ needs and want and delivering the desired satisfactions better than competitors do.
- Societal concept: Marketing strategy should deliver value to customers in such a way that improves both customers as wells as society’s well-being and long-run interests.
Step 3: Constructing an integrated marketing plan that delivers superior value
The company’s marketing strategy outlines which customers the company will serve and how it will create value. Then the marketer develops integrated marketing plans that will the intended value to target customers.
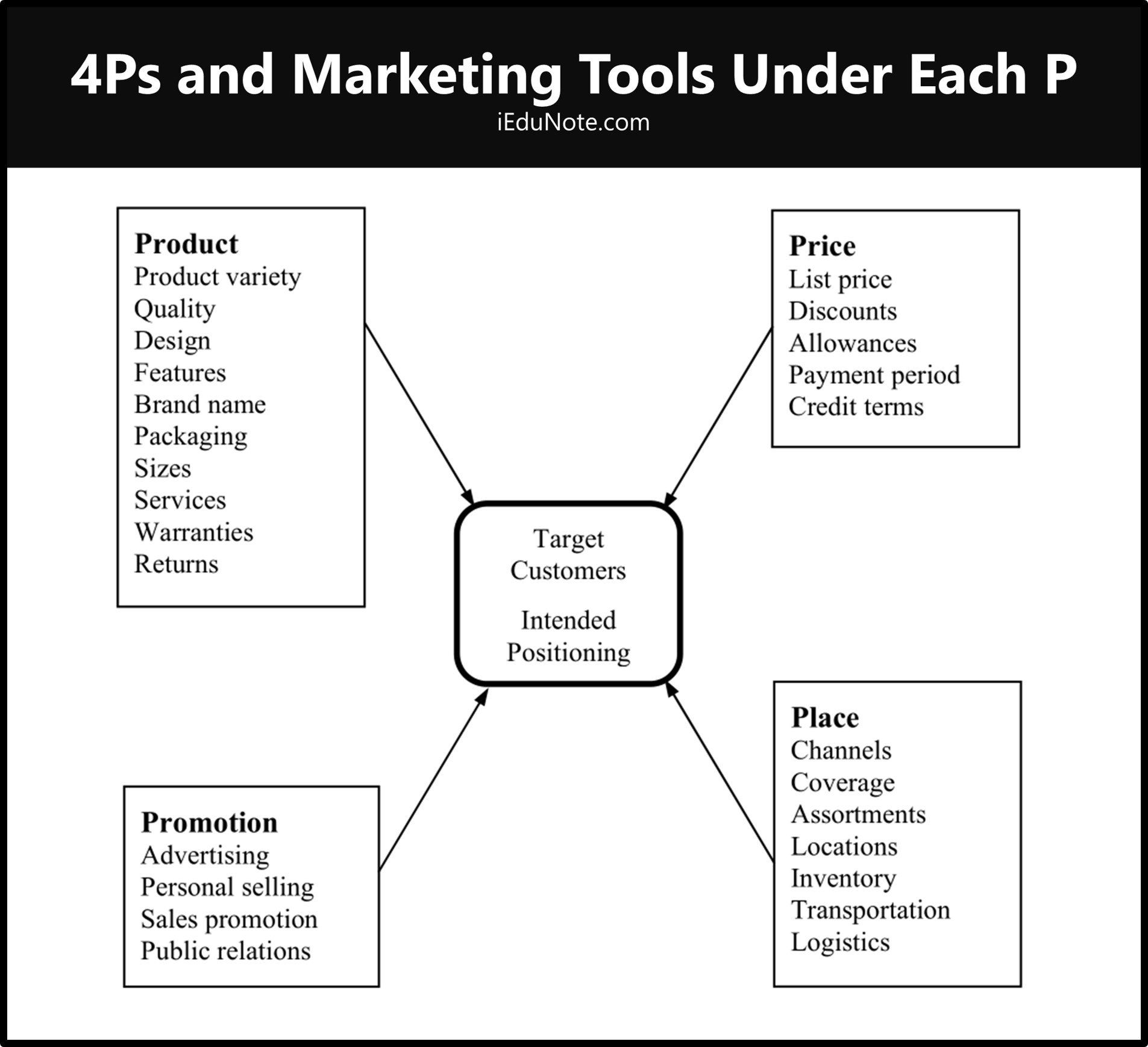
It consists of the firm’s marketing mix (4Ps), the set of marketing tools the firm uses to implement its marketing strategy.
The marketing program builds customer relationships by transforming the marketing strategy into action.
For this, it needs to blend all of these marketing tools into a comprehensive, integrated marketing program that communicates and delivers the customers’ expected value.
Step 4: Build Profitable Relationships
Customer relationship management is the overall process of building and maintaining profitable customer relationships by delivering superior customer value and satisfaction.
Customer relationship management aims to produce high customer equity, the total combined customer lifetime values of all of its customers.
The key to building lasting relationships is the creation of superior customer value and satisfaction.
Companies today want to acquire profitable relationships and build relationships that will increase their share of the customer portion of the customers purchasing that a company gets in its product categories.
Step 5: Capturing Value From Customers
Customer relationship management’s ultimate aim is to produce high Customer equity – total combined lifetime values of all of the company’s current and potential customers.
The more loyal to the company’s profitable customers, the higher are the customer equity. Customer equity may even be a better way to measure its performance than market share or current sales.
Marketers cannot create customer value and build customer relationships by themselves. They need to work closely with other company departments and with partners outside the firm.
In addition to being good at customer relationship management, they also need to be good at partner relationship management.
Final Words Managing Marketing Process
The last step of the marketing process is arranging the resources necessary to carry out the marketing plan, putting the plan in action, and exerting control.
For the implementation of the marketing plan, the firm needs to build a marketing organization.
This type of organization consists of many specialists responsible for carrying out marketing research, advertising, product development, customer service, etc.
Such an organization calls for setting up a department called the marketing department headed up by a Vice-President/Director/GM. He usually performs three types of tasks.
First, he coordinates activities performed by different personnel in the marketing department.
Second, he must closely work with other key personnel charged with other responsibilities, such as personnel, finance, etc.
Third, he must perform several operative and technical functions as selecting, training, directing, motivating, and evaluating his department’s personnel for better performance by each of them.
When the plan is implemented, management must make sure that everything is going fine. He can ensure this by receiving feedback and taking corrective action if necessary, i.e., controlling.