Cost accounting is the process of ascertaining and accumulating the cost of a product or activity. It involves accounting for the classification, analysis, interpretation, and control of cost.
So, it is a system of accounting that provides information about the ascertainment and control of costs of products or services. It measures the operating efficiency of the enterprise. It is an inner aspect of the enterprise.
What is Cost Accounting?
Cost accounting is the process of accounting from the point at which expenditure is incurred or committed to the establishment of its ultimate relationship with cost centers and cost units.
In the widest usage, it embraces the preparation of statistical data, application of cost control methods, and the ascertainment of profitability of activities carried out or planned.
Costing includes the techniques and processes of ascertaining costs.
The technique refers to principles that are applied to ascertain the costs of products, jobs, processes, and services. The ‘process’ refers to day to day routine of determining costs within the method of costing adopted by a business enterprise.
Costing involves the classifying, recording, and appropriate allocation of expenditure for the determination of costs of products or services, the relation of these costs to sales value; and the ascertainment of profitability. Cost Accounting, a subject that provides management with information relating to costs, is a service to management.
Management of a manufacturing or service organization, private sector or public sector organization, profit-making or non-profit-making organization, the military or civilian organization would make sure that cost accounting is accorded the necessary attention it deserves.
Cost Accounting Cycle
The cost accounting cycle is a process performed during the accounting period in recording data, classifying, determining total cost, determining product cost, determining selling price, controlling cost, and decision making.
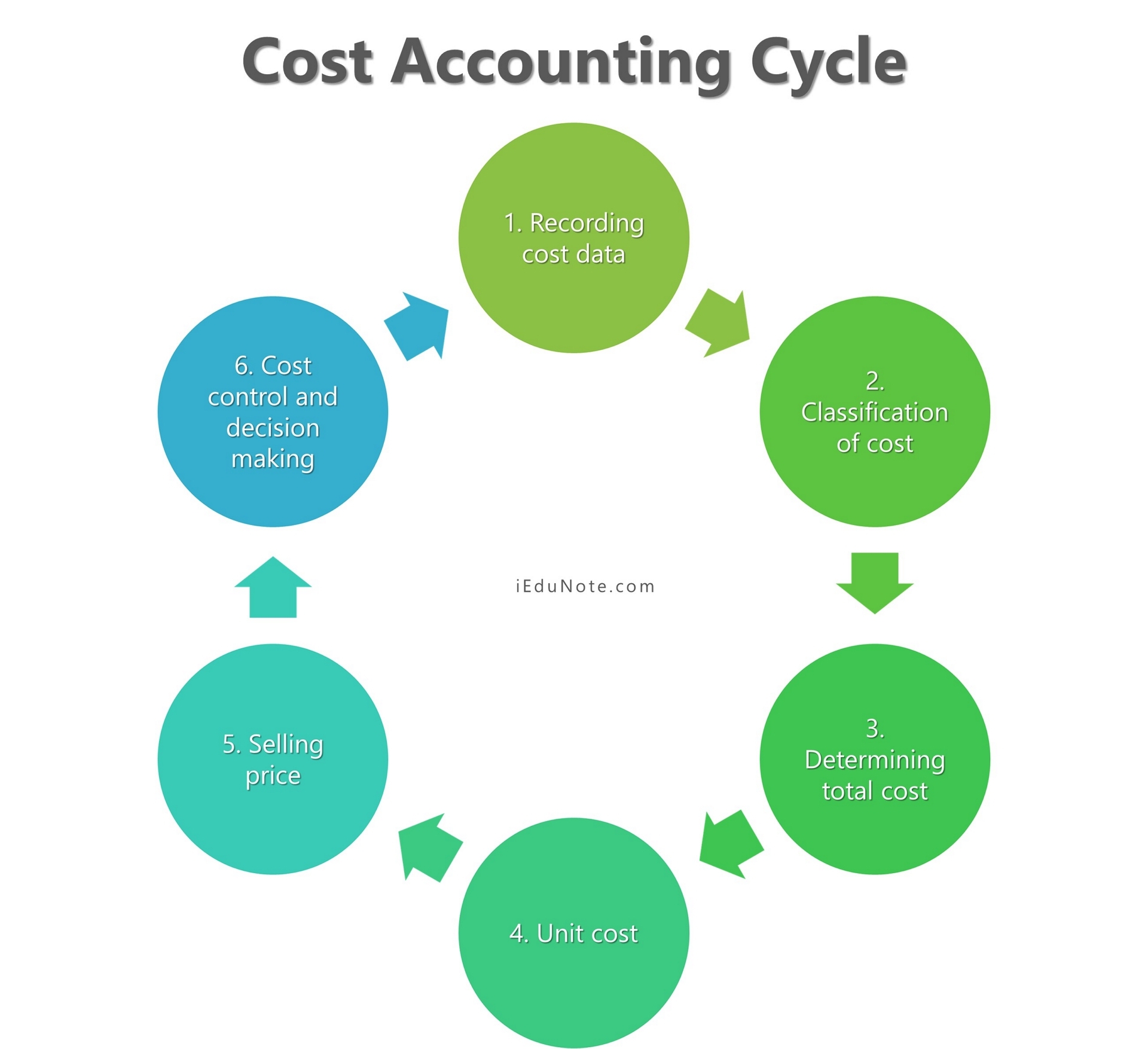
Recording cost data
At the first step of cost accounting, it ascertains and records the element of cost for determining of cost of production.
Classification of cost
In the second step, according to function, nature, and behavior, cost accounting classifies the cost.
Determining total cost
In this step, under cost accounting cost of goods sold of a product is calculated.
The cost of goods sold means the sum of all items of expenditure incurred in production for the goods which are sold.
Unit cost
In the fourth step, the Unit cost is obtained by by dividing the cost of goods sold by the total number of units sold.
Selling price
The selling price is obtained by adding a profit margin to the cost of sales.
Cost control and decision making
At the last step of cost accounting, using standard costing and budget and budgetary control system, cost accounting controls cost and makes a decision.
Characteristics of the Cost Accounting System

The characteristics of ideal cost accounting are shown and explained below;
Correctness
The system of cost accounting should provide the correct information in terms of both cost ascertainment and presentation. Otherwise, it will mislead the users.
Ease
The cost accounting system involves a detailed analysis of cost. To avoid complications in the procedure of cost ascertainment, an elaborate system of costing should be avoided, and every care must be taken to keep it as simple as possible.
Elasticity
The cost accounting system should be capable of adapting itself to the changing situations of business. It must be capable of expansion or alteration depending on the needs of the business.
Cost-effectiveness
The costs of operating the costing system must be cost-effective and economical. The benefit should be out weight than cost.
Comparability
The records to be maintained must facilitate comparison over some time. The records must serve as a basis to guide the future.
Promptness
An ideal costing system is one that provides cost data in an analytical form to the management.
So all the departments of the factory must analyze and record the relevant items of cost quickly to furnish cost information regularly to various levels of management.
This helps in checking up on the progress of the business regularly.
Periodical preparation of accounts
To facilitate the comparison of results frequently, it is desirable to prepare accounts periodically.
Constant comparison of actual results with standard results enables to spot of areas of inefficiency. This can be set right by taking remedial measures.
Reconciliation with financial accounts
The system of cost accounts must be capable of reconciling with financial accounts to check the accuracy of both systems of accounts.
Uniformity
The various forms and documents used under the costing system must be uniform in the size and quality of the paper. Printed forms must be used to avoid delays in the preparation of reports.
This also reduces the burden on clerical staff. Forms of different colors can be used to distinguish different documents.
Objectives of Cost Accounting
There is a relationship among the information needs of management, cost accounting objectives and techniques and tools used for analysis in cost accounting.
- Ascertainment of cost.
- Controlling cost.
- Ascertainment of Profitability.
- Classification of Cost.
- Fixation or Selling Prices.
- Facilitating preparation of financial and other statements.
Cost accounting has the following main objectives to serve:

Ascertainment of cost
Cost ascertainment involves the collection and classification of cost in the first step. Those items of expenses that are capable of charging directly to the products manufactured are allocated.
Then the other expenses which are not capable of direct allocation are apportioned on a suitable basis. Thus the cost of production of goods manufactured is ascertained.
Controlling cost
Cost accounting helps in attaining the aim of controlling cost by using various techniques such as Budgetary Control, Standard costing, and inventory control.
Each item of cost [viz. material, labor, and expense] is budgeted at the beginning of the period, and actual expenses incurred are compared with the budget. This increases the efficiency of the enterprise.
Ascertainment of Profitability
Cost accounting helps in ascertaining the costing profit or loss of each product, process, job, operation or service rendered on an objective basis by matching cost with the revenue of the activity.
The statement of profit or losses and Balance Sheet are also submitted to the management periodically.
Classification of Cost
Cost accounting classifies cost into different elements such as materials, labor, and expenses. It has further been divided as a direct cost and an indirect cost for cost control and recording.
Fixation or Selling Prices
Cost accounting guides management regarding the fixation of selling prices of the products. It is also helpful for preparing tenders and quotations.
Facilitating preparation of financial and other statements
Cost accounting helps to produce statements at short intervals as the management may require.
The financial statements are generally prepared once a year or half-year to meet the needs of the management.
To operate the business at high efficiency, it is essential for management to have a review of the production, sales, and operating results.
Cost accounting provides daily, weekly, or monthly statements of units produced and accumulated cost with analysis. The cost accounting system provides immediate information regarding the stock of raw materials, semi-finished and finished goods.
This helps in the preparation of financial statements.
Role / Importance / Advantages of Cost Accounting
The limitation of financial accounting has made the management to realize the importance of cost accounting:-
- It helps in cost reduction.
- Ascertainment of cost.
- Benefits of the National Economy.
- Fixation of responsibility.
- Price fixation.
- Inventory controls.
- Elimination of wastage.
- It helps in checking the accuracy of the financial account.
- Facilities cost comparison.
- Helps in the estimate.
The role/importance/ advantages of cost accounting are discussed in below:

Helps in cost reduction
The cost can be reduced in the long run when cost reduction programs and improved methods are tried to reduce costs.
Ascertainment of cost
Cost accounting helps the management in the ascertainment of the cost of the process, product, Job, contract, activity, etc., by using different techniques.
Identifying unprofitable activities: With the help of cost accounting, the unprofitable activities are identified so that the necessary corrective action may be taken.
Benefits of the National Economy
An efficient costing system benefits the national economy by increasing government revenue and achieving higher production. The overall economic developments of a country take place due to the efficiency of production.
Fixation of responsibility
For appropriate cost accounting, cost centers and responsibility centers are determined.
Price fixation
By using demand and supply, activities of competitors, and market conditions to a great extent, also determining the price of the product and cost to the producer does play an important role. The producer can take the necessary help from his costing records.
Inventory controls
Cost accounting helps to control costs by using techniques like a perpetual inventory system, ABC analysis, economics order quantity, etc.
Elimination of wastage
As it is possible to know the cost of the product at every stage, it becomes possible to check the forms of waste, such as time and expenses, etc, in the use of machine equipment and material.
Helps in checking the accuracy of financial account
Cost accounting helps in checking the accuracy of financial accounts with the help of reconciliation of the profit as per financial accounts with the profit as per cost account.
Facilities cost comparison
Costing accounting enables management to make cost comparisons of various jobs, products, departments, etc., to improve performance.
Helps in estimate
Costing records provide a reliable basis upon which tender and estimates may be prepared.
Cost accounting has become an essential tool for management
Cost Determination
Cost Accounting is used to determine the cost per unit of different products of a business concern which is helpful for the management of any company.
Cost Control
The technique of cost control is of recent development.
Cost Accounting is used for cost control due to with it a manager of any organization can easily identify the real situation of an organization. That’s why cost accounting is an essential tool for management.
Help in management decision making
Cost accounting provides a correct analysis of cost by the processor operations. So we can say that, cost. Accounting can help the manager of any organization in decision-making.
Fixation of price
By cost, the accounting manager can get the proper information about the production cost of any product, which can help him in fixing a product price.
Profit determination
Administration can ascertain their profit by analyzing the cost of an organization’s manufacturing process, which is only determined by cost accounting.
Budget & Planning
In an organization, cost accounting can be used as a good element for ascertaining the cost of production, which means, the cost of direct material, direct labor, and direct expenses, and the data or information of that cost accounting can be helpful for budgeting and planning for the senior management.
Difference between Cost Accounting and Financial Accounting
Both financial and cost accounting are in agreement concerning actual cost data and product costing analysis. The value of ending inventory and the cost of goods produced and sold are the main examples.
For the preparation of financial statements, a financial accountant receives the necessary data from the cost accountant.
Despite there are several differences between cost accounting and financial accounting.
The Difference between Cost Accounting and Financial Accounting are;
| Basis | Cost Accounting | Financial Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Objective | It provides information about the ascertainment of cost to control the cost and for decision making. | It provides information about the financial result and financial position of the business. |
| Scope | It is suitable only for such business concerns which are engaged in manufacturing, production, mining’ or providing some service (e.g. bus company electric supply company). | It is suitable for all businesses – manufacturing, production or even in marketing only. |
| Pre-determined and historical accounting | In cost accounting, the expenditure to be incurred is estimated and the standard cost of a product is found. Thus, it acts as a pre-determined process. | In Financial Accounting, accounting is done based on historical cost. |
| Nature of transactions | Transactions related to production activities only are accounted for in this method. Donations, dividend received, etc. are not taken into account as these are not related to production. | All economic transactions are taken into account, whether these are related to production or not. |
| Selling Price | By cost accounting, the price of the product can be fixed more accurately in a scientific manner. | In the absence of information about cost, the selling price fixed by this method may be misleading. |
| Profit & Loss | The profit calculated by this method expresses the result of production activities. | Profit calculated by this method expresses the profit of the organization. |
| Information about cost | Full and correct information about the cost, per unit cost, various elements of cost, etc. of the product is made available in cost accounting. | Financial accounting does not give such detailed and correct information. |
Differences between Cost Accounting and Managerial Accounting
Generally, the terms management accounting and cost accounting are considered to be interchangeable. This is accepted since the two fields are interrelated.
Moreover, one is a part of the other. Besides this, cost and management accounts are utilized in the same context.
The information available from cost accounts is needed by the management also, especially for stock valuation, order assessment, and pricing decisions.
Technically speaking, the cost function is complementary to the management function. The differences between Cost Accounting and Managerial Accounting are given below;
| Issues | Cost Accounting | Management Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cost Accounting is the process of recording, classifying and allocation of cost for the determination of costs of products and services. | Management Accounting may be defined as the function of accounting techniques for providing information intended to help all levels of administration in forecasting and controlling the actions of a business organization and in decision making. |
| Objectives | The primary objective of cost accounting is to determine the cost of producing a product or providing service. | Management accounting is to provide information to the management for planning, controlling, and decision making. |
| Data Used | Only quantitative data are recorded in cost accounting. | Management accounting uses both’ quantitative & qualitative information. |
| Nature | Cost accounting is based on past & present facts and figures. | Management accounting deals with plans based on past & present cost data. |
| Focus | Cost accounting focuses on understanding and optimizing costs in a complex business environment. | Management accounting focuses on the bigger picture of using data to make planning and strategy decisions for the ‘ company. |
|
Provide information | Provide information to both internal & external users. | Provide information to internal users. |
| Importance |
To be competitive in a global economy, companies must optimize material, labor and overhead costs. Cost accounting for a production process can help identify inefficient activities and improve productivity while also lowering cost. | Management accounting is used for internal managerial decision making, project selection, budgeting, performance evaluation, and strategy. |
Due to the difference between cost and management accounting, it is more appropriate to refer to them collectively as Cost and management accounting.
The term highlights the relation between these two areas but simultaneously recognizes their differences.
Cost and management accounting are useful for planning, control, and decision-making purposes.
Factors to Be Considered in Selecting Method of Remuneration/incentive plan
- The wage system should be the best combination of the interests of both the employer and the employees. From the employer’s point of view, the cost of labor should be the minimum with the maximum qualitative output. From the worker’s angle, the wages should be fair and equitable and should be an adequate reward for the efforts put in by them. The workers should also be allowed to share the profits of prosperity periods in the form of increased wages or bonuses.
- Workers must get a minimum wage under the system. Moreover, the system should provide incentives for an efficient worker to arouse his interest further in the work. Thus, the human factor should be given due prominence.
- The wage system should be easy to understand and simple to operate. Complex calculations may arouse suspicion in the minds of illiterate laborers.
- Flexibility in the system of wage payment is an essential factor to be considered so that the system may be changed suitably whenever required.
- Incentive schemes should be introduced for both direct and indirect workers. In case of direct workers, the measurement of performance does not involve any problem. However, in the case of indirect workers, viz. supervisors, machine maintenance, stores, internal transport workers, etc., there is no appropriate method for their performance evaluation. Hence, introduction of an incentive scheme in their case is a bit difficult. It is still essential to provide incentives to such workers also for increasing their efficiency and promoting team spirit. Monetary incentives to direct workers may be in the form of profit sharing or co-partnership, or co-ownership scheme, while monetary incentives for indirect workers can be in the form of bonuses to different categories of indirect workers on an appropriate basis.