Business is a term with a very wide meaning. It refers to an activity of people working for the purpose of producing and distributing goods and services at a profit. A business activity creates utilities by the production of goods and services to satisfy human wants.
Simply, business is an activity of people directed towards satisfying human wants at a profit. In a broad sense, business is the activity performed by an individual or a group of people with a view to earning profit within the government rules and regulations.
Let’s understand business and its definition, elements, functions, features, objectives, and importance.
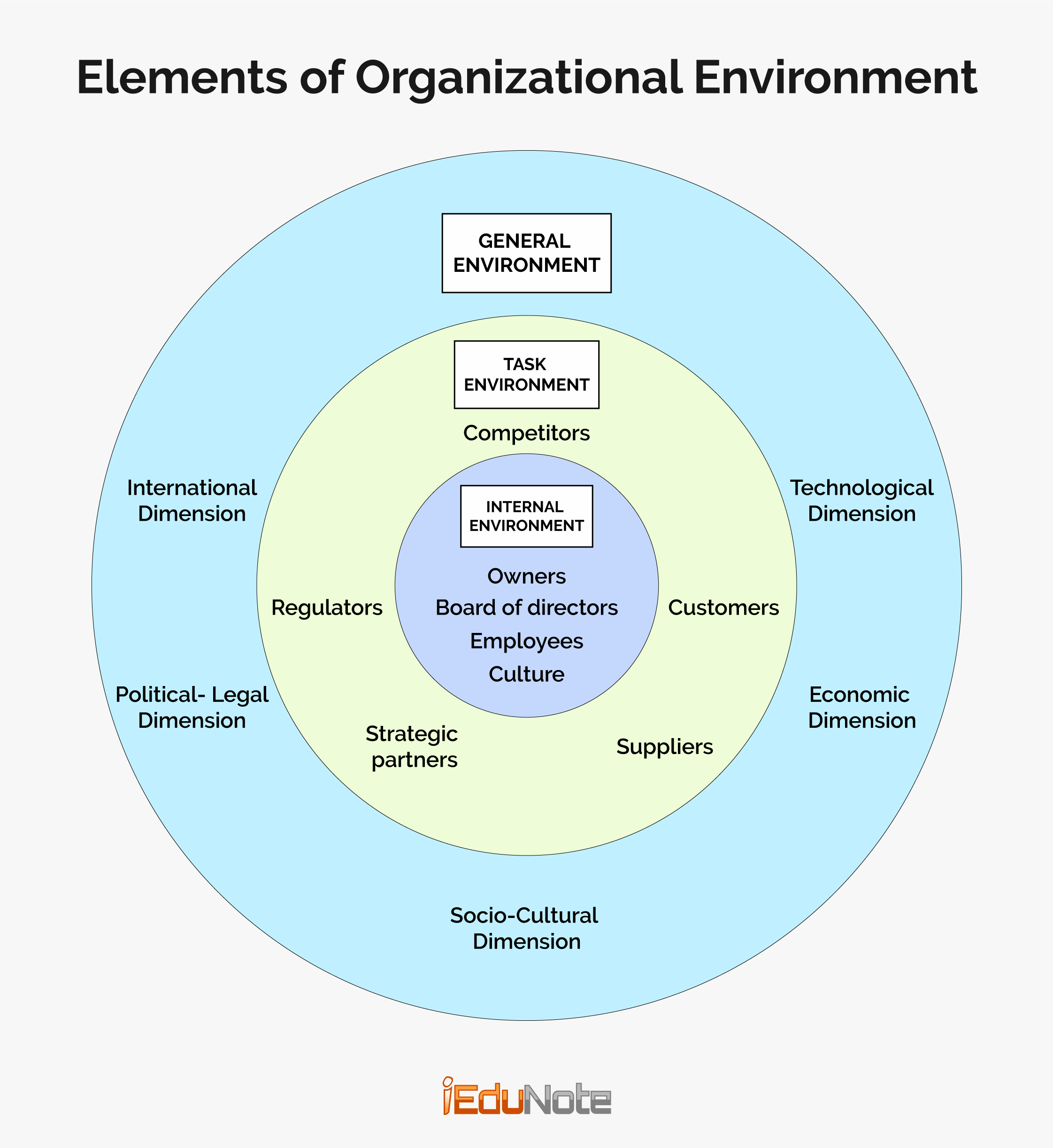
Business Is Society
Next to love and religion, business is considered the most significant factor influencing human life. Although Allah (SWT) created us for “Obadiah” (Worship) under the guidance of Al-Quran and Sunnah, we are madly involved in serving our desires provoked by the traditional business firms under their ulterior motives!
This is why human civilization is there- where it should not be! And since today’s business is the business of business, the ultimate purpose of business is to create customers, not to satisfy their demands or maximize their satisfaction!
Consequently, to do so, business firms strive to convert human beings into ‘economic people’ who are born to consume and ‘win’ in society in the form of satisfying their material and spiritual demands.
We have been trapped by the business subconsciously but magnifying it with so-called prudence.
This is all about the prevailing business domain, not the ‘desired’ business domain, as encouraged by Allah (SWT), being 80% of human ‘Rizq’ (Provision) reserves in business.
However, if we leave alone the philosophical aspects of business and speak in the tone of business scholars, we would have to glorify it and define business as the process of creating some utilities and distributing those utilities to earn a profit and to make the customer loyal.
The process includes production/ buying and selling/distribution. More specifically, where production is absent, and buying takes place.
A business cannot create any matter. The matter is the gift of nature. What businesses can do is simply add some utilities to the gift of nature by changing their shape, size, quality, or quantity.
The utilities may be formed utility, place utility, time utility, possession utility, financial utility, and utilities against risk.
Commonly utilities refer to production, and place utilities refer to distribution.
What is Business?
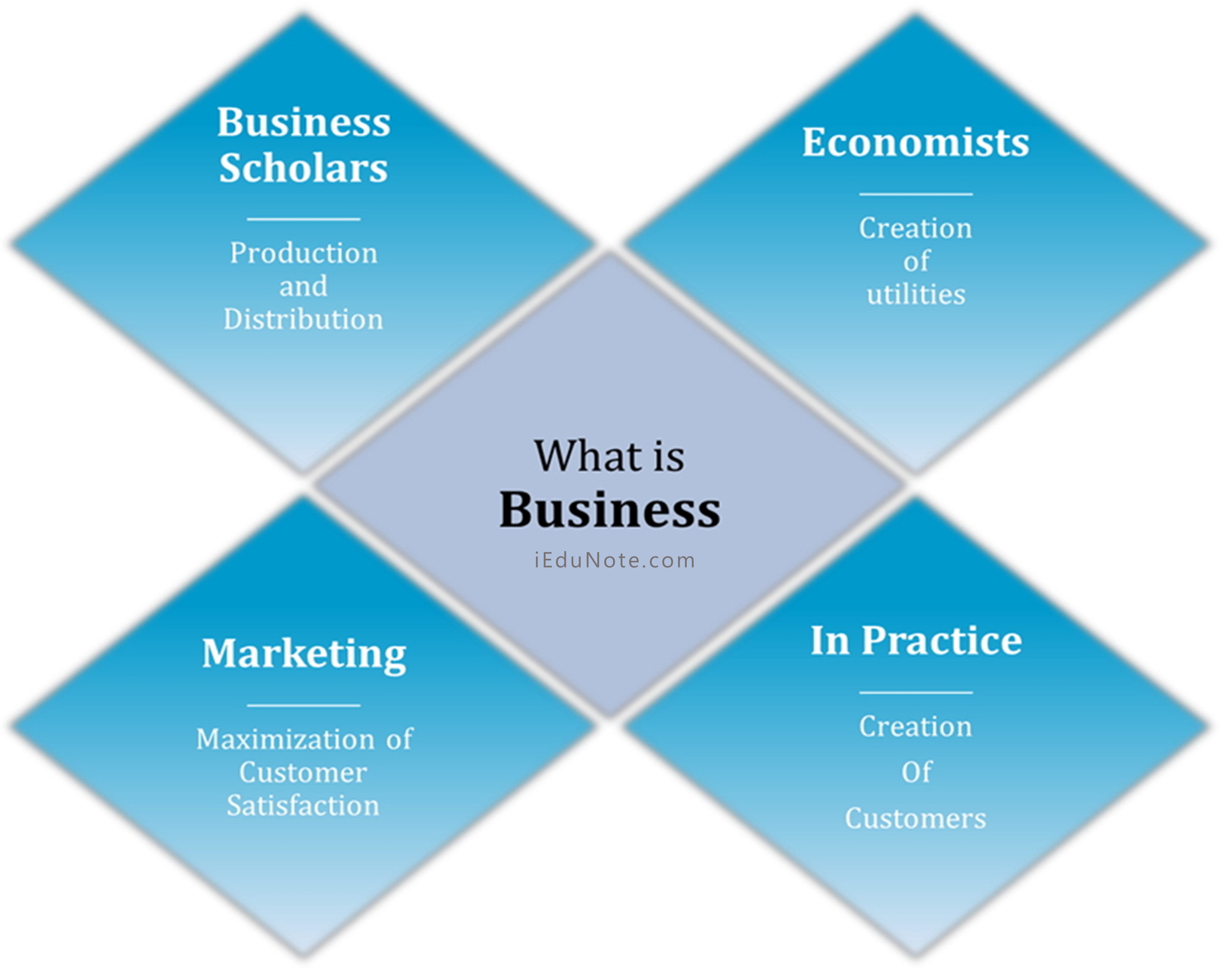
Business without profit or loss is no business. It is the whole complex field of trade, commerce, industry, and the network of ancillary services, distribution, banking, insurance, transport, and so on, which serve and penetrate the world of business as a whole.
Koontz and Fulmer define business as “Any person, group company or government department or agency whose purpose is to produce or sell products or services.
According to Keith and Carlo, “Business is a sum of activities involved in production and distribution of goods and services for private profits.”
An n the words of Ivancevich and Skinner, “Business is of exchange of goods, services, or money for mutual benefit ai profit.”
According to Robert. N. Owens, ‘Business is an enterprise engaged in the production and distribution of goods for sale in the market or rendering services for profit.”
According to Skinner and Ivancevich; “Business is the exchange of goods, services, or money for mutual benefit or profit.”
According to Keith Davis; “Business may be defined as any form of commercial activity to satisfy the economic wants of people at a profit.”
Professor Owen defined; “Business as any enterprise engaged in production and distribution of goods for sale in a market or rendering services for a price.”
Business refers to any economic activity directed toward the creation of values for satisfying the demands of the customer (people) through regular production and exchange of goods and services with the object of earning a profit.
Elements of Business
The essentials of starting a business, which is abstract, are called elements of the business. Some of the elements are discussed below:
Business idea
Every business starts with an idea. The idea needs to be justified in respect of its practicability and lucrativeness.
Entrepreneurship
The birth of business requires some sort of entrepreneurship. It is equally applicable irrespective of the nature and size of the enterprise.
Forecasting
A business plan is a written description of the expected future of the business. Forecasting helps in preparing a business plan.
Organization
Land, labor, and capital are the scattered means of production that are arranged, correlated, and coordinated by the entrepreneur to turn the idea into reality.
Uncertainty
In the free-market economy, uncertainty is inevitable since there exists competition in the field of production as well as in distribution.
Legality
The production and distribution, i.e., the business, need to be legalized. To do so, it has to go through a legal framework.
Profit-seeking motive
All activities of the business, such as procurement, production, or creation of utilities, distribution, etc., are guided by the profit-seeking motive, i.e., a surplus of income over expenditure.
Financing
Whether large or small, every business requires two types of capital – fixed capital and working capital. Thus, the business requires ensuring finance at the lowest cost.
Research and Development (R&D)
To be ahead and increase the market share, R&D remains the only alternative for the business enterprise.
Customer Satisfaction
The business organization ensures customer satisfaction through the creation of utilities.
Functions of a Business
The primary function of business is to create utilities so that it can satisfy human wants. In addition to utility creation, the following are the important functions of the business:
Risk-Taking Function
In business, at every moment, there is a chance of loss.
For example, the price of the product may fall suddenly. There is also a chance of property destruction. So, an important function of a businessman is that he takes the risk and starts the business.
Management
The basic function of the businessman is to manage the business. Management solves many problems like starting, operating, planning, staffing, and controlling the business.
Management has to provide direction to all subordinates.
Planning
A business firm needs to plan what is to be produced. When and for whom is it to be produced?
Financial Function
Money plays a very important role in business. Without capital, a businessman can not establish and expand the business.
When a firm has not a sufficient amount, it borrows the money from banks and other financial institutions to operate the business. Credit control loans, wages, purchase, and sale discounts are financial functions.
Innovative Functions
Today there is stiff competition in the business market. Innovation is essential for business advancement.
A businessman keeps in view the needs and wants of the consumer, introduces new goods according to the demands of the peoples.
So he tries to find out new production techniques and new forms of business organization. Payment of Rent Wages and Interest A businessman hires factors like land, labor, and capital to produce goods and services. He pays the reward to these factors in the shape of rent, wages, and interest.
Production Function
A businessman combines the factors of production and produces the goods with the object of earning a profit. A businessman conducts this process for his profit.
Use of Technology
A businessman also uses technology and new methods of production according to the nature of his business. It increases his profit.
Optimum Combination A businessman tries to combine the factors of production in such a way that the cost of production remains at a minimum and profits up to the maximum level.
Improvement of quality
A businessman also improves the quality of the product to increase his sales. Otherwise, he will suffer loss.
Sales Function
It is a very difficult job for the businessman because there is hard competition in the market. Noteworthy, a businessman also performs various other duties before selling, like grading, sorting, and packaging.
Transportation and Communication Function
Transportation and communication functions are performed by the businessman. It involves the transfer of goods from one hand to another in exchange for money.
Social Function
In urban areas, pollution is increasing due to industrial expansion. So businesses should also share the cost of pollution. It is the responsibility of businesses to reduce pollution as part of social function.
Sound Organization
There is a need for a sound organizational structure for the business. It will use the sources properly and will increase profit and production.
Motivation
Motivation is an important function of a business. It encourages employees to give their best performance to achieve the objectives.
To sum up, all these functions are necessary for ensuring customer satisfaction and to win in the battle of competition.
Features/Characteristics of Business
Although business organizations differ in many ways, they have a common feature: the ‘conversion-transformation’ of inputs (resources) into outputs (goods or services).
In addition to conversion, the following are the common features of business concerns:
Deals in goods and services
People in business are engaged in the production and distribution of goods and services. The goods may be consumer goods like bread, butter, milk, tea, etc., or capital goods like a plant, machinery, equipment, etc.
The services may be in the form of transportation, banking, insurance, warehousing, advertising, and so on.
Sale or exchange of goods and services
If a person produces or buys a product for self-consumption or for gifting it to another, he is not engaged in business. But when he produces or buys goods to sell it to somebody, he is engaged in business.
Thus, in business, the goods and services produced or purchased must be exchanged for money or goods (under the barter system between the buyers and sellers.
Without the sale or exchange of goods, the activities cannot be treated as a business.
Regular exchange of goods and services
The production or buying and selling activities must be carried out regularly. Normally, an isolated transaction is not treated as a business.
For example, if Adam sold his old Toyota car to Moses, it is not considered business unless he continues to buy and sell cars regularly.
Requires investment
Every business activity requires some amount of investment in terms of land, labor, or capital. These resources are utilized to produce a variety of goods and services for distribution and consumption.
Aims at earning profit
Business activities are performed with the primary objective of earning income by way of profit.
Without profit, it is not possible to survive for a long period. Earning of profit is also required to grow and expand the business.
Involves risk and uncertainty of income
We know that every business aims at earning a profit. The businessman who invests the various resources expects a fair amount of return.
But, despite his/her best effort, the reward he/she gets is always uncertain.
Sometimes, he/she enjoys profits, and also, times may come when he suffers heavy losses. This happens because the future is unpredictable, and the businessman has practically no control over certain factors.
Business Objectives/Goals
It is generally believed that a business has a single objective, that is, to make a profit. But it cannot be the only objective of a business.
While pursuing the objective of earning a profit, business units do keep the interest of their owners in view.
However, any bush ess unit cannot ignore the interests of its employees, customers, the community, or society as a whole.
For instance, no business can prosper in the long run unless fair wages are paid to the employees and customer satisfaction is given due importance.
Again a business unit can prosper, only if it enjoys the support and goodwill of people in general.
Business objectives also need to be aimed at contributing to national goals and aspirations as well as towards international well-being.
Thus, the objectives of business may be classified as:
- Economic Objective.
- Social Objectives.
- Human Objectives.
- National Objectives.
- Global Objectives.
Economic Objectives
Economic objectives of business refer to the objective of earning profit and also other objectives that are necessary to be pursued to achieve the profit objective, which includes the creation of customers, regular innovations, and the best possible use of available resources.
Economic objectives also include;
- Growth and Expansion
- Exploration of new market
- Better service to retain an existing customer
- R & D
- Adoption of the latest technology
- Targeted return on investment
Social Objectives
In the words of Henry Ford, “The primary objective of business should be service, and its subsidiary aim should be earning of profits.” That means the focus is on the social objectives of a business.
Social objectives are those objectives of a business that are desired to be achieved for the benefit of society. Since business operates in society by utilizing its scarce resources, society expects something in return for its welfare.
No activity of the business should be aimed at giving any kind of trouble to society.
If business activities lead to socially harmful effects, there is bound to be a public reaction against the business sooner or later.
Social objectives of business include production and supply of quality goods and services, adoption of fair trade practices, contribution to the general welfare of society, and provision of welfare amenities.
Other social objectives are:
- Sufficient return to investors.
- Protecting the interest of stakeholders.
- Avoiding unfair tax and VAT practice.
- Paying a fair dividend to shareholders.
- Protecting the environment.
Human Objectives
Human objectives refer to the objectives aimed at the wellbeing as well as the fulfillment of expectations of employees as well as of people who are disabled, handicapped, and deprived of proper education and training.
The human objectives of business may thus include the economic well-being of the employees, social and psychological satisfaction of employees, and the development of human resources.
The human objective also includes:
- To provide an opportunity for employees to participate in decision-making relating to their interests.
- To ensure fair wages and incentives.
- To provide a better working environment for employees.
- To ensure growth opportunities for employees.
National Objectives
Every business must have the objective of fulfilling national goals and aspirations.
The goal of the country may be to provide employment opportunities to its citizens, earn revenue for its exchequer, become self-sufficient in the production of goods and services, promote social justice, etc.
Business activities should be conducted with these goals of the country in mind, which may be called the national objectives of a business.
Global Objectives
Earlier socialist countries had a very restricted business relationship with other nations. There was a very rigid policy for the import and export of goods and services.
But, nowadays, due to liberal economic and export-import policy, restrictions on foreign investments have been largely abolished, and duties on imported goods have been substantially reduced.
This change has brought about increased competition in the market. Today, because of globalization, the entire world has become a big market.
Goods produced in one country are readily available in other countries.
So, to face the competition in the global market, every business has certain objectives in mind, which may be called global objectives.
Thus, we may sum up, in the words of Urwick, “Earning of profits cannot be the objective of a business any more than eating is the objective of living. Rather, all business organizations should ensure sufficient effort to achieve the above objectives of a business.”
Importance/Role of Business in Socio-Economic Development of a Country
Business is the process of creating wealth under the incentive of private gain. It leads to innovations and improvements to enrich the lives of people.
Based on it, the importance of business can be discussed in the following ways;
Supplier of goods and services
Business firms supply goods and services to society.
Utilization of resources
It utilizes society’s resources for the production of goods and services.
Capital formation
Business firms are responsible for capital formation in the economy.
Employment generation
Providing employment opportunities to a large number of members of society, business firms increase total national income.
Standard of living
Businesses help in improving the standard of living by supplying better quality of goods and services.
Government revenue
Business firms provide tax revenue to the government of the country and enable it to undertake development projects and programs for the welfare of the citizens.
Social justice
Employees of the business firms spend a major part of their active lives in the organization.
In return for ensuring a safe, healthy, and humane work environment for the employers, some organizations are ensuring social justice.
Encouraging creativity and growth
In its interest, some business organizations encourage the creativity of employees, which leads to their career growth and advancement.
Creating a scope for high caliber (freedom seeker):
Those people who are high caliber in nature, freedom seekers, and who bring about changes in the society and economy are allowed to step towards their way through the business.
Changes in benchmarking
The concept of benchmarking is no longer limited to the national boundary, and it goes to a global perspective.
As a result, local firms are to compete internationally since their benchmark is international.
Scope of Business
The scope of business is very comprehensive. It encompasses all human activities that tend to satisfy the needs and wants of the human beings living in a society. A large part of the business is concerned with providing the final or finished products or goods to the desired people.
Business is universal and everywhere.
It is essential to ensure the production and distribution of goods, and services to satisfy the economic wants of people at a profit. The nature and scope of business are changing very quickly.
The people who are engaged in business must cope with the changing environment because the people’s -attitudes, habits, tastes, likes and dislikes, norms, beliefs, values, perceptions, and motives are changing with the change of time.
Profit earning cannot be the sole motive of business activity.
Businessmen do have a social responsibility, too, that must be met.
Business organizations produce goods and services to generate profit but such activities create impact on society as well as the whole community. The responsibility of a businessman is to provide goods and services in a way that is not harmful to society.
Prerequisites of a Successful Business Organization
Business profit is not only the output of entrepreneurial effort; it is the logical sequence of favorable factors called prerequisites of business profit.
Let us for those:
- Market Condition.
- Availability of Capital.
- The scale of production.
- Form of Organization.
- Selection of Location.
- Government Policy.
- Concessions.
- Availability of Raw Material.
- Availability of Labor.
- Availability of Machines.
- Means of Transportation and Communication.
- Administrative Conditions.
- Formulation of Business Policy.
Market Condition
First of all, businessmen keep in view the demand for the goods which they want to produce and keep in view their skills and experience.
If the demand is inelastic, then the chances of success are bright.
Availability of Capital
Capital is considered an important factor in the business. It is required for the purchase of land, machines, wages, and raw materials.
A businessman has to decide before starting the business how much capital he can arrange.
The scale of production
Before starting the business, a businessman also decides that he has to produce the goods on a small scale or large scale. He makes the decision keeping in view the availability of capital and demand for the goods.
Form of Organization
A businessman also has to decide about the form of organization. He may start the business as a sole proprietor as a partnership, or in the form of a joint-stock company.
Selection of Location
A businessman selects the place for business, keeping in view the availability of raw materials, cheap labor, and transportation.
If these things are easily available, then he will start the business there.
Government Policy
The attitude of the government towards the business is also considered by the businessman. If the government encourages business, then it will be profitable for the businessman.
Concessions
Sometimes, the government provides loans at a low rate of interest to particular industries. Sometimes, the tax holiday is provided in particular areas.
So a businessman also considers the government, concessions before starting the business.
Availability of Raw Material
A businessman should also keep in view the availability of raw materials. If it is imported from other countries, then it may create problems for him.
Availability of Labor
Before starting the business, a businessman should also consider the availability of labor. If skilled and efficient labor is not available, then the business will not be profitable.
Availability of Machines
A businessman should also examine whether the machines required for the business are available inside the country or not. If these will be imported, then the government will provide the foreign exchange or not.
Means of Transportation and Communication
If the means of transportation are quick and cheap, then the cost of production will be low, and the rate of profit will be high.
The expansion of the market also depends upon the quick and cheap means of production.
Administrative Conditions
The success of a business depends upon the administration. If the administration is efficient and capable, then the rate of profit will be high in the business.
So, a businessman should pay proper attention to the administrative aspect of the business.
Formulation of Business Policy
A businessman also frames the policy about the methods of payments, receipts, and techniques of production. These are essential for a successful business.
Conclusion
Profit earning cannot be the sole motive of business activity. Businessmen have a social responsibility that must be met. Moreover, the business organization produces goods and services to generate profit.
At the same time, it must have some impact on society as well as the whole community. The responsibility of a businessman is to provide goods and services in a way which are not harmful to society. Another responsibility of businessmen is to supply goods and services at a fair price.