The main objectives of the audit are to examine the financial statements and express opinions on the correctness of financial positions.
The objective of an audit is to express an opinion on financial statements, to give the opinion about the financial statements, the auditor examines the financial statements to satisfy himself about the truth and fairness of the financial position and operating results of the enterprise.
There are certain inherent limitations of audit examination. It would not be possible for any type of auditor to discover all errors and frauds in the financial statements due to the limitations of his checking.
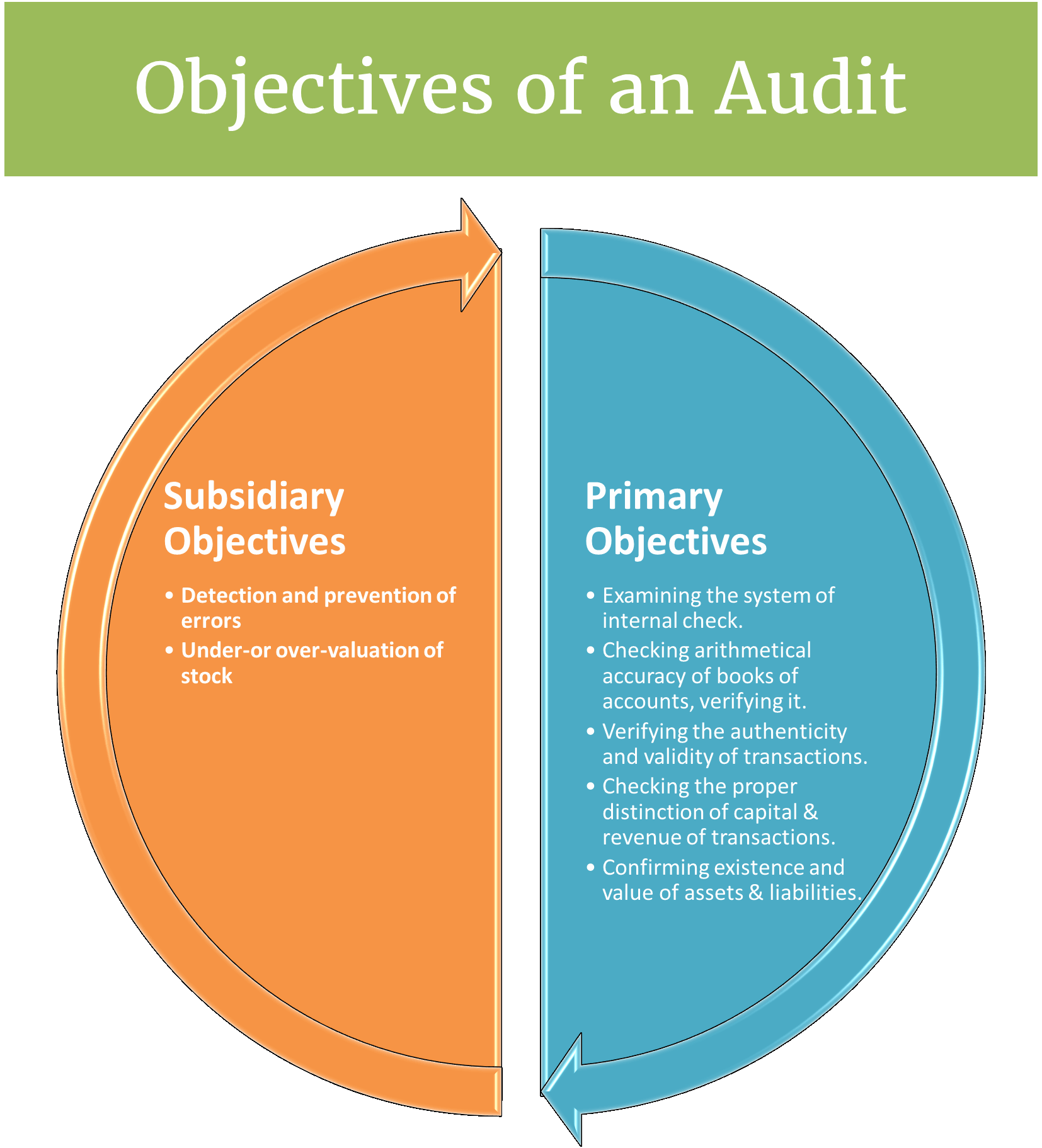
Such discovery is not the main objective of the audit. An audit has 2 objectives.
Primary Objectives of Audit
The main objectives of the audit are known as the primary objectives of the audit. They are as follows:
- Examining the system of internal checks.
- Checking arithmetical accuracy of books of accounts, verifying posting, casting, balancing, etc.
- Verifying the authenticity and validity of transactions.
- Checking the proper distinction between the capital and revenue nature of transactions.
- Confirming the existence and value of assets and liabilities.
Verifying whether all the statutory requirements are fulfilled or not.
Proving truth and fairness of operating results presented by income statement and financial position presented by the balance sheet.
Subsidiary Objectives of Audit
These are such objectives that are set up to help in attaining primary objectives. They are as follows:
Detection and prevention of errors
Errors are mistakes committed due to carelessness, negligence, lack of knowledge, or without a vested interest.
Errors may be committed without or with any vested interest.
So, they are to be checked carefully. Errors are of various types. Some of them are:
- Errors of principle.
- Errors of omission.
- Errors of commission.
- Compensating errors.
Detection and prevention of fraud
Frauds are those mistakes that are committed knowingly with some vested interest in the direction of top-level management.
Management commits frauds to deceive taxes, to show the effectiveness of management, to get more commission, to sell a share in the market, or to maintain the market price of the share, etc.
Detection of fraud is the main job of an auditor.
Such frauds are as follows:
- Misappropriation of cash.
- Misappropriation of goods.
- Manipulation of accounts or falsification of accounts without any misappropriation.
Under-or over-valuation of stock
Normally such frauds are committed by the top-level executives of the business. So, the explanation given to the auditor also remains false.
So, an auditor should detect such frauds using skill, knowledge, and facts.
Other objectives
- To provide information to the income-tax authority.
- To satisfies the provisions of the Companies Act.
- To have a moral effect.