The COVID-19 pandemic has changed how organizations operate globally. Remote work has become essential to overcome challenges from the pandemic and employees’ preferences. Remote work has many benefits, including high employee satisfaction, increased productivity, and cost savings.
However, many organizations have not embraced remote work, and HR managers can play an important role in motivating employees to adopt remote work strategies. Our goal is to enable HR managers to coordinate with other managers and remote workers to work efficiently and effectively, realizing the benefits of remote work.
Let’s Learn how remote working continuously changes the workplace and human resource management.
Impact of COVID-19 on Working Practices
The global coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic has transformed overall working practices and processes in different organizations.
Employees who never considered remote working opportunities are bound to work from home using modern and ever-changing technologies and processes such as computers, telephones, mobile phones, robots, Zoom, MS Teams, Google Meet, etc.
The remote working opportunity is also called a significant process to give employees the freedom to work from home or any other location they prefer.
However, we argue that whether it is the freedom to work from anywhere or the opportunity to spend more time with family, Generation Y and Generation Z employees would want more than a traditional 9-to-5 job.
Hence, the demand for and development of remote working strategies is now inevitable for every organization to overcome the challenges originating from different sources such as the pandemic, generational employees’ convenience, employees’ cost consciousness, the nature of organizations, etc.
Remote Working: A New Norm
Instead of commuting to an office every day to perform duties at a designated desk or job location, many employees would prefer and gain the capability to design a work-life experience that works for them and for increasing the size of the workforce in today’s generation, which has created the option: ‘working remotely.’
Hence, remote work has gained significant popularity over the last decade; for example, 42 million out of 144 million workers in the United States of America (USA) could have done their job at home in 2018, which is 29% of the total workforce!
This trend is not only apparent in the case of the USA but also in many other developed and emerging countries where remote working strategies are being applied by organizations not only to allow employees freedom or better work-life experience but also to boost productivity and employee retention.
Challenges of Remote Working
Besides the increasing demand for flexible work options, remote working also has many benefits, such as high employee satisfaction and loyalty towards employers, better-increased productivity, and cost savings.
Still, many organizations in several countries haven’t fully embraced remote working.
This is also evident from our country’s perspective, where technological development and digitalization have seen a dramatic surge among the people, especially the professionals of different organizations, in the last few years. However, due to the current COVID-19 pandemic, many companies have had to allow workers to work from home using various technologies and processes.
However, due to a lack of knowledge regarding remote working, its full benefits are not being gained by stakeholders of different organizations.
The scenario is no different in the case of our HR managers. However, it is felt that top management support could play a significant role in motivating employees to embrace remote working strategies.
Hence, we have endeavored to clarify the concept, showing some challenges and solutions relating to remote working.
Empowering HR Managers for Remote Work Implementation
We strongly believe that our efforts would benefit the HR managers and those who are about to implement remote working practices and manage remote workers in our country.
Our ultimate goal is to enable HR managers to help coordinate with other managers and remote workers to enable them to work efficiently and effectively, thereby realizing the benefits of remote working.
History of Remote Work
There have been a number of arguments about conceptualizing and measuring various forms of remote work.
However, the idea of remote working emerged during the oil Crisis in the early 1970s when American Jack Nilles and colleagues outlined how reduced commuting could save the national economy. Remote work (remote working) has different definitions, and some of them are listed below;
ILO (1990) defines remote work as telework in a place far from the essential office. Therefore, employees would be separated from personal and physical communication with colleagues. The new technology would lead to division using communication facilities.
International Association of Remote Working defines remote working as a work pattern in which the employees are flexible in terms of time (part-time or full-time) and the place (home, remote sites, or mobile form) to perform responsibility and respond to duties.
Remote working is also not only a work but also a process of instituting work that is developed around information dealing out.
Therefore, employees are away from company colleagues, service providers, or clients, do a job that involves using a range of electronic tools, and engage a person, product, or the result of a remote pass.
Benefits of Remote Work
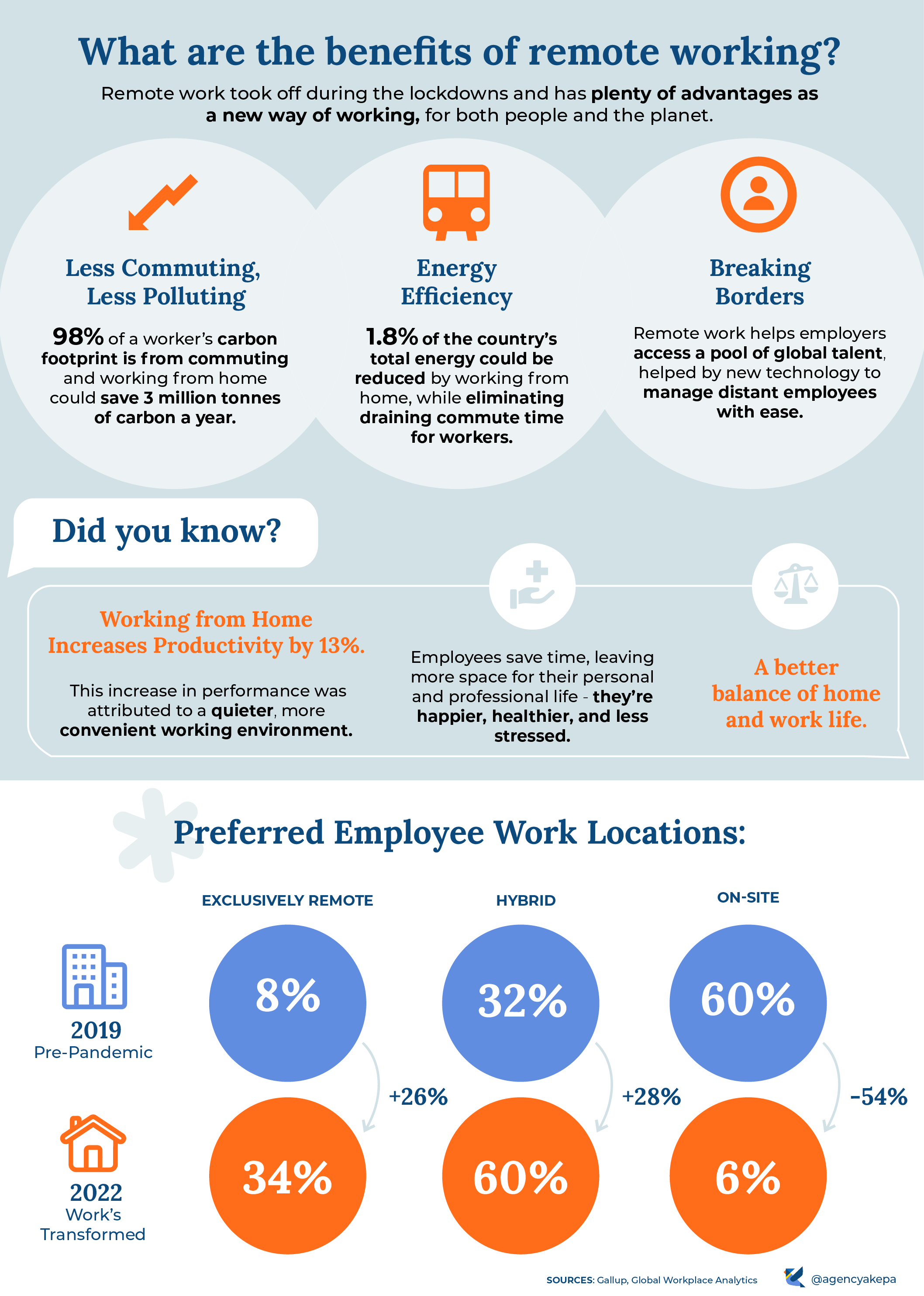
Remote work is not only useful for accomplishing various jobs remotely (i.e., from home or other locations) but is also identified as beneficial to the development of the balance of employees. Furthermore, this process can also develop the employees’ engagement, productivity, and retention, especially for millennials (i.e., Generation Z).
Sustainability and Health Benefits of Remote Work
Kinman et al. argued that although some professionals struggle to adjust to remote working practices due to the new work environment, for example, at home, working remotely is, in the long run, sustainable and healthy.
For example, it facilitates the process of work of many departments in organizations to continue their functions even during the pandemic situation and can be exercised in post-pandemic workplaces.
Enhancing Business Resilience and Capability
Furthermore, remote work can bolster organizations’ business capability to keep operations running and safe from unforeseen situations like COVID-19. Remote working has also contributed a lot to creating a new normal working environment that is more adjustable than any other process among many companies, especially in developed countries.
Therefore, it is high time to develop remote work strategies in all organizations, regardless of their size and country.
Impact on Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
Remote working practices (working from home or other locations outside of the actual work location) are also effective in keeping the smaller organizations (i.e., SMEs) running during the pandemic and also keeping ready for any other future pandemic as well. It is because, being smaller in terms of size, these organizations are more vulnerable to closure due to any pandemic.
As a result, the resilience of SMEs and even other organizations would be very much stronger in response to any kind of disaster or challenging situation when full practical or physical work would not be possible.
Work-Family Balance and Cost Savings
Furthermore, remote work is also effective for the development of the work-family balance, which has been very challenging in the current modern world where employees have less time to enjoy with their family members.
Moreover, remote working is beneficial because it eliminates the waste of commuting time while it also contributes to the reduction of expensive office space rent and arrangement.
Promoting Flexibility and Diversity through Remote Work
Furthermore, flexible working practices are developed through remote working practices, including a diverse workforce from different geographical locations (i.e., countries).
Thus, it may be argued that remote work can benefit both the sponsoring organization and the remote workers because of flexibility and cost-effectiveness.
How to build remote work?
There are some arguments about the conceptualization and measurement of various types of remote working practices or strategies, and therefore, building remote work in an organization would also be different according to organizational capabilities.
The differences could also be due to the external stakeholders of the organizations and unique projects because not all the projects would be compatible with all sorts of remote work elements or instruments.
The advancement of technologies (i.e., remote working technologies, for example, software, computers, phones, and so on) has facilitated the development of remote work for managers, especially HR managers in organizations.
However, a higher level of capabilities is to be taken into consideration for the successful implementation of remote working.
The model shown below for successful remote work has been adapted from the Nickson & Siddons. A range of software tools that are normally adopted to build efficient and effective remote work in organizations has been outlined below:
| Tool/Software | Purpose | What the team is used for |
|---|---|---|
| Skype for Business | Personal voice calls / Video calls / Group voice calls / Group video calls | Used in integration with Outlook, mainly for video calls during meetings – mainly daily stand-ups and retrospectives. |
| ZOOM | Personal voice calls / Video calls / Group voice calls / Group video calls / Conference call | Used primarily for individual and group audio or video calls. |
| MS Teams | Personal voice calls / Video calls / Group voice calls / Group video calls / Conference call | Used primarily for individual and group audio or video calls. |
| Google Meet | Personal voice calls / Video calls / Group voice calls / Group video calls / Conference call | Used primarily for individual and group audio or video calls. |
| Outlook | Email / Calendar | Used primarily for setting up tasks, meetings in the Outlook calendar – the meeting reminders are synchronized, and thus all team members are aware of the various scheduled project-related activities. |
| PHPStorm | Integrated Development Environment (IDE) | Used for writing, debugging, and testing PHP code. Often used in conjunction with SourceTree and Bitbucket. |
| MySQL | Database | Used as a backend for the PHP-based online system. Test environment of the database used extensively for debugging code with dummy data. |
| WebEx | On-demand collaboration, Online meeting, Web conferencing, and video conferencing | Used for show & tell sessions per release that included all the project teams in the company and also sales teams. |
| Bitbucket | Online Git repository | Used for code collaboration and source control, pull requests, code review, and code commits. The code review comments appear inline against the code and allow interactive conversations about the code to take place online. |
Challenges in Implementing Remote Working Practices
Implementing remote work practices in different organizations or any other developing country could be challenging due to limitations in financial and human resources.
Difficulty in managing remote workers is another barrier that demotivates organizations to develop remote working practices.
Besides, the lack of required logistics for remote workers is also a significant challenge in implementing remote working practices, especially in Bangladesh, where a scarcity of durable technologies and continuous internet exists.
Cultural and Social Barriers to Remote Work
Furthermore, resistance from employees’ families is also identified as significant in developing remote working practices by many organizations.
Also, the career prospects for employees working remotely may suffer due to reduced physical presence and interaction with fellow colleagues, and thus, getting employees for remote work can also be difficult.
Ethical and Flexibility Concerns in Remote Work
Moreover, maintaining and following ethical standards may be challenging when companies or organizations adopt remote work practices.
Flexibility from remote working practices among employees may also encroach on main job duties, especially when they are at home. Therefore, the real advantage of remote work may not be achieved as expected.
Communication and Monitoring Challenges
Miscommunication between managers and employees is also common in a remote work culture in executing various functions, and thus, reducing miscommunication is very challenging for organizations with remote work facilities.
This challenge is also supported by the studies conducted by Dery & Hafermalz (2016) and Coffey & Wolf (2018), who found that a transparent communication process is difficult with the employees when they are out of the regular work to get the work done.
Moreover, monitoring functions performed by employees to check quality and outcome becomes difficult, and therefore, many organizations do not attempt to implement remote working practices.
Managerial Resistance and Data Security Concerns
Furthermore, managerial resistance to adopting remote working practices at different levels (in bigger organizations) has also been found to be a big challenge for many companies. It is because remote work increases managerial responsibilities; for example, in communication (using phones, emails, and other modes is increased), monitoring, and supervisory responsibilities online.
Maintaining personal and organizational data security is another significant challenge of remote working strategies; hence, many companies would not be interested in implementing remote work.
Solutions in Implementing Remote Working Practices
Studies focusing on solutions to the challenges in implementing remote working practices are rare, especially concerning developing countries.
However, providing training to the employees on various remote working devices and processes could be effective in developing the efficiency of working virtually. It would also improve the employees’ interest in adopting remote working practices.
The Importance of Ongoing Training
In this regard, training should be organized periodically because remote work tools keep updating or changing. As a result, employees would be familiarized and capable of using updated tools, i.e., technologies and processes from their homes, to perform various jobs.
Ethical Standards and Logistics Support
Furthermore, preparing and applying organizational ethical standards integrating remote working practices can also be effective in ensuring that the remote work endeavor harms no one. There has always been a complaint regarding a lack of logistics support with the required facilities when organizations adopt remote work.
Therefore, it is also critical to provide all logistics to ensure that employees have everything to get the best out of remote work arrangements.
Monitoring and Motivation Strategies
Furthermore, employees may also occupy themselves with other sorts of software, for example, gaming on computers when they are online.
Hence, regular monitoring becomes essential. Providing technologies such as computers, mobile phones, software, and WiFi for smooth internet (high bandwidth), as well as financial incentives, would enable and motivate employees to welcome and start remote work.
Emotional Support and Data Security
Moreover, emotional support to the employees with all sorts of communication is also crucial in the implementation and success of remote working practices.
Furthermore, reviewing and updating data security aspects are also recommended as an effective solution to ensure hackers or outsiders cannot steal valuable information from the systems.
Government and Academic Support for Remote Work
Recent studies have also outlined that the government can play a pioneering role in developing remote work by passing laws for online work arrangements.
In this respect, the government should also provide financial, technological, and HR support so that the adopting organizations can cope with the extra burden of developing and establishing remote work.
Moreover, universities in different countries can also offer short courses on remote work for all students so that they can adapt to remote work in the professional world.
Selecting Remote Workers
The selection of remote workers would be different from traditional employee selection because the nature of the work to be done is different, and also remote working is not suitable for all jobs.
Therefore, HR managers of organizations should know some information, structure, and content to select remote workers. Hence, we provide some insights for managers of organizations planning remote work.
Addressing Ethical and Safety Concerns for Remote Workers
Managers should clarify the potential employees regarding ethical, health & safety issues that would be different for remote workers because many organizations cannot ensure the safety and ethical obligations when employees work from home or any other location.
Assessing Home Office Suitability and Policy Optimization
Furthermore, managers should also assess the suitability of the home office for employees to work remotely either by visiting the homes or based on employees’ explanations.
The organizational policies, terms, and conditions that may apply to expenses and so on should also be optimized before selecting remote workers.
Navigating Tax Issues for Remote Workers
Furthermore, tax issues are very significant and different in the case of remote workers because of their personal situations and location. Many people in Bangladesh work as remote workers for foreign firms and pay taxes twice!
Therefore, if any organization in Bangladesh recruits remote workers (especially with high skill, which is rare in Bangladesh) from developed countries, management must clarify all these tax-related issues to avoid any kind of misunderstanding.
All these issues are generally different from the issues relating to traditional works. These are crucial issues to be settled by managers with the potential remote workers during selection.
Adapting to Remote Works During Pandemic Situation
COVID-19 has caused many difficulties, and stakeholders are trying to find solutions by introducing financial support, training, and skill development initiatives.
Several impediments are hindering the process of adjustments, such as absence of commitment, financial constraints, communication problems, lack of skills, and training.
The reality suggests that proper initiatives will ease the current adversity, and we can expect to have at least a new normal situation instead of the traditional one because of these impediments.
The entire process of adjustments, the roles of stakeholders, and the consequences have been delineated in the above figure, emphasizing that remote working practices can be effective in adapting to new normal work periods.
It is also important to remember that although the “new normal” work environment mainly originated from the COVID-19 pandemic situation, revolutionary technological change can also help create another “new normal” work environment about which we cannot even think.
Hence, adopting remote work would be the best approach for organizations so that any changes can be warmly welcomed and applied to execute different functions.
Future of Remote Work and Its Impact
Remote work is our new reality since the COVID-19 outbreak urges employers to adopt remote work rapidly. It is obvious that remote work would have significant potential to keep businesses operational during any pandemic. Remote working practices can save costs, promote employees’ well-being, and save the environment.
However, some significant challenges exist in implementing remote working practices in countries like Bangladesh.
Therefore, it is high time to take the necessary initiatives to develop remote working practices in order to keep business operations running during any unexpected situation. In this regard, the solutions stated in this chapter can effectively implement remote working practices.
However, the rise of remote work might become a new norm that will affect and influence not only employees and managers but the overall productivity and sustainability of the organizations. It is also very significant to argue that the variety of remote workers will increase with the development of Internet facilities.
For example, 5G Internet would facilitate surgeries by doctors from different countries. In this respect, the surgeons would be the remote workers!
Therefore, there is no scope to think that remote workers would not only deal with computers for security, data entry, communication, and supervision but also with many other significant and high-skilled jobs from remote locations.

