A lease is a contract under which one party, the lessor (owner of the asset), gives another party (the lessee) the exclusive right to use the asset, usually for a specified time in return for the payment of rent.
Leasing is the process by which a firm can obtain the use of certain fixed assets for which it must make a series of contractual, periodic, tax-deductible payments. A lease is a contract that enables a lessee to secure the use of the tangible property for a specified period by making payments to the owner.
Major Features of Lease
The major features or elements of the leasing are the following:
- The Contract: There are essentially two parties to a contract of lease financing, namely the owner and the user.
- Assets: The assets, property to be leased are the subject matter lease financing contract.
- Lease Period: The basic lease period during which the lease is non-cancelable.
- Rental Payments: The lessee pays to the lessor for the lease transaction is the lease rental.
- Maintain: Provision for the payment of the costs of maintenance and repair, taxes, insurance, and other expenses appertaining to the asset leased.
- Term of Lease: The term of the lease is the period for which the agreement of lease remains in operation.
- Ownership: During the lease period, ownership of the assets is being kept with the lessor, and its use is allowed to the lessee.
- Terminating: At the end of the period, the contract may be terminated.
- Renew or Purchase: An option to renew the lease or to purchase the assets at the end of the basic period.
- Default: The lessee may be liable for all future payments at once, receiving title to the asset in exchange.
Advantages of Lease Financing
The advantages from the viewpoint of the lessee
- Saving of Capital: Leasing covers the full cost of the equipment used in the business by providing 100% finance. The lessee is not to provide or pay any margin money as there is no down payment. In this way, the saving in capital or financial resources can be used for other productive purposes, e.g., the purchase of inventories.
- Flexibility and Convenience: The lease agreement can be tailor-made in respect of lease period and lease rentals according to the convenience and requirements of all lessees.
- Planning Cash Flows: Leasing enables the lessee to plan its cash flows properly. The rentals can be paid out of the cash coming into the business from the use of the same assets.
- Improvement in Liquidity: Leasing enables the lessee to improve its liquidity position by adopting the sale and leaseback technique.
- Shifting of Risk of Obsolescence: The lessee can shift the risk upon the lessor by acquiring the use of assets rather than buying the asset.
- Maintenance And Specialized Services: In the case of a special kind of lease arrangement, the lessee can avail specialized services of the lessor for maintenance of asset leased. Although lesser charges higher rentals for providing such services, leases see overall administrative and service costs are reduced because of specialized services of the lessor.
- Off-the-Balance-Sheet-Financing: Leasing provides “off-balance-sheet” financing for the lessee in that the lease is recorded neither as an asset nor as a liability.
The advantages from the viewpoint of the lessor
There are several extolled advantages of acquiring capital assets on lease:
- Higher profits: The Lessor can get higher profits by leasing the asset.
- Tax Benefits: The Lessor being the owner of an asset, can claim various tax benefits such as depreciation.
- Quick Returns: By leasing the asset, the lessor can get quick returns than investing in other projects of the long gestation period.
Disadvantages of Lease Financing
The disadvantages from the viewpoint lessee
- Higher Cost: The lease rental includes a margin for the lessor as also the cost of risk of obsolescence; it is, thus, regarded as a form of financing at a higher cost.
- Risk: Risk of being deprived of the use of assets in case the leasing company winds up.
- No Alteration in Asset: Lessee cannot make changes in assets as per his requirement.
- Penalties On Termination of Lease: The lessee has to pay penalties in case he has to terminate the lease before the expiry lease period.
The disadvantages from the viewpoint of lessor
- High Risk of Obsolescence: The Lessor has to bear the risk of obsolescence as there are rapid technological changes.
- Price Level Changes: In the case of inflation, the prices of an asset rise, but the lease rentals remain fixed.
- Long term Investment: Leasing requires the long term investment in the purchase of an asset and takes a long time to cover the cost of that asset
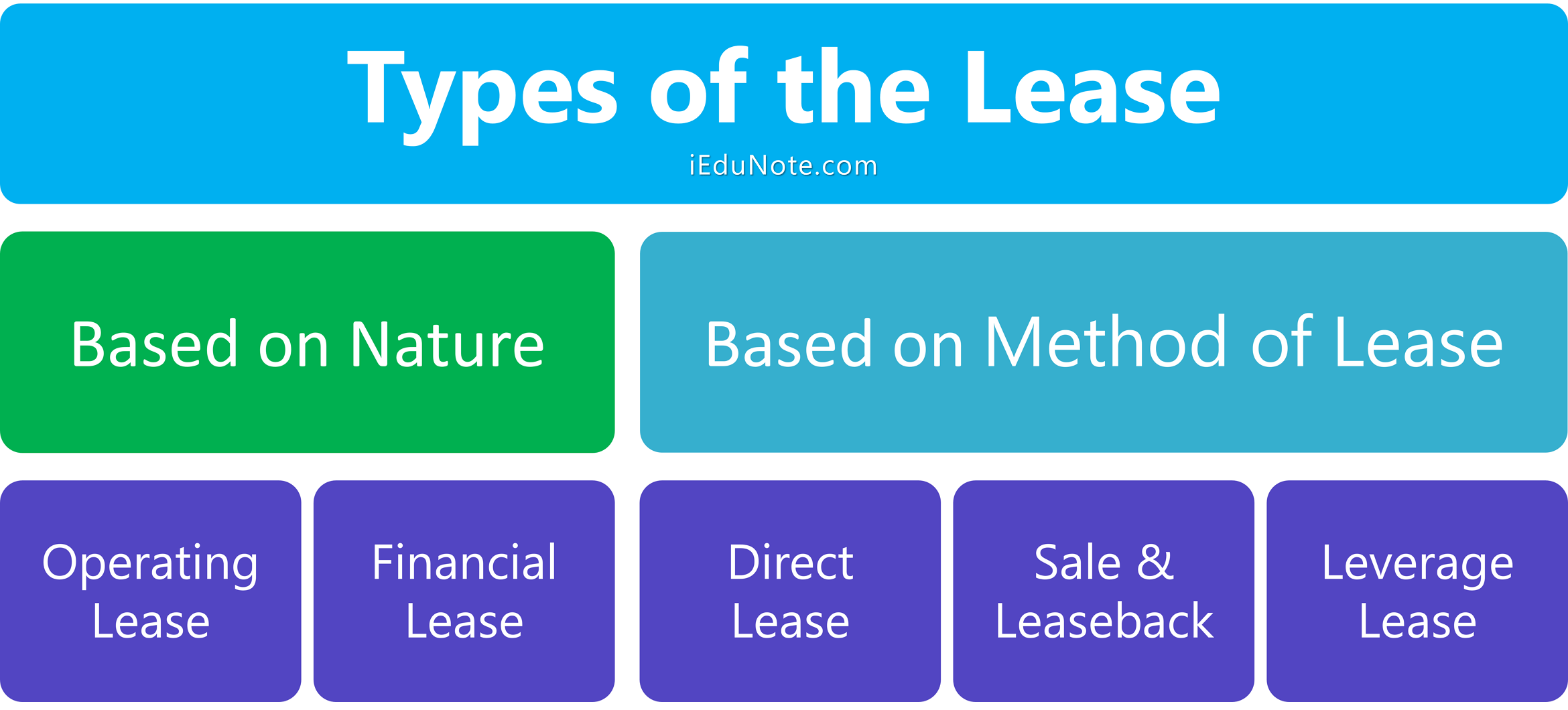
Types of the Lease
Leasing takes different types, which are given below;
- Based on Nature.
- Operating lease.
- Financial lease.
- Based on the Method of Lease.
- Direct lease.
- Sale & Leaseback.
- Leverage lease.
- Operating Lease: An operating lease is a cancelable contractual agreement whereby the lessee agrees to make periodic payments to the lessor, often for 5 or fewer years, to obtain an asset set’s services. According to the International Accounting Standards (IAS-17), an operating lease is one that is not a finance lease.
- Financial Lease: A financial (or capital) lease is a longer-term lease than an operating lease that is non-cancelable and obligates the lessee to make payments for the use of an asset over a predetermined .period of time. According to the International Accounting Standard (IAS-17), in a financial lease, the lessor transfer to the lessee substantially all the risks and rewards identical to the ownerships of the asset whether or not the title is eventually transferred.
- Direct Lease: Under direct leasing, a firm acquires the right to use an asset from the manufacture directly. The ownership of the asset leased out remains with the manufacture itself.
- Sale & Leaseback: Under the sale & leaseback arrangement, the firm sells an asset that it owns and then leases to the same asset back from the buyer. This way, the lessee gets the assets for use, and at the same time, it gets cash.
- Leveraged Lease: Leveraged lease is the same as the direct lease, except that a third party, the lender, is involved in addition to the lessee & lessor. The lender partly finances the purchase of the asset to be leased; the lessor turns to be a borrower.
Distinguish between the Operating and Financial Lease
| Topics | Operating Lease | Financial Lease |
| Definition | An operating lease is short term lease used to finance assets & is not fully amortized over the life of the asset. | A financial lease is the lease used in connection with long-term assets & amortizes the entire cost of the asset over the life of the lease. |
| Duration | Short term leasing | Long term leasing |
| Cost | The lessor pays the maintenance cost. | Lessee pays the maintenance cost. |
| Cancel & Changeable | Cancelable lease & It is a changeable lease contract. | Non-cancelable lease & It is not a changeable lease contract. |
| Risk | lessor bears the risk of the asset. | The lessee bears the risk of the asset. |
| Purchase | At the end of the asset is hot purchasable. | At the end of the contract, the asset is purchasable. |
| Renew | It is a renewable contract. | It is not a renewable contract. |
| Also called | Service lease, short term lease, cancelable lease. | A capital lease, long term lease, non-cancelable lease. |
So, from the above discussion, we can say that lease is a contract under which one party the lessor (owner) of an asset, agrees to grant the use of that asset to the lessee in exchange for periodic rental payments. The rent is a tax-deductible expense.
Features of Lease Arrangements That Cause Unique Accounting Problems
The features of lease arrangements that cause unique accounting problems are:
- Residual values.
- Sales-type leases (lessor).
- Bargain-purchase options.
- Initial direct costs.
- Current versus noncurrent classification.
- Disclosure.