The Stapel scale is used as an alternative to the semantic differential, especially when it is difficult to find bipolar adjectives that match the investigative question.
The scale places a single adjective in the center of an even number of numerical values (ranging from +3 to -3).
It measures how close or distant a given stimulus is perceived to be from the adjective.
The table below illustrates a Stapel scale item used in the measurement of the attitude of the student toward a class teacher:
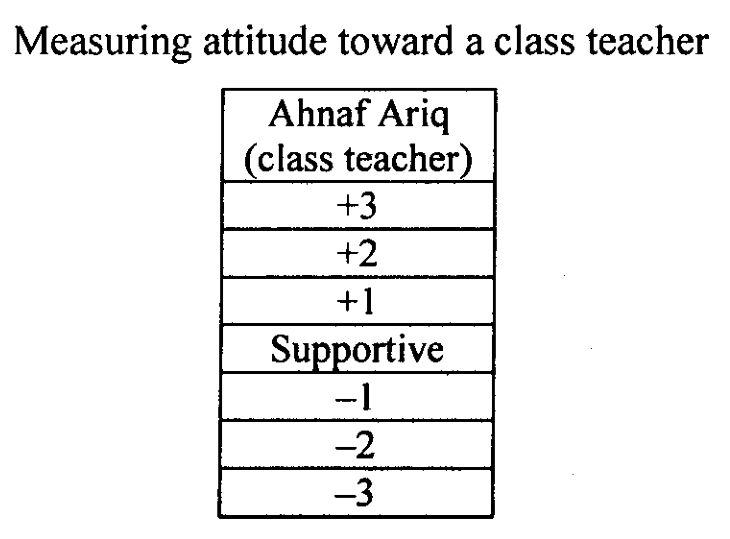
Respondents select a plus (+) number for the characteristic that describes the named teacher. The more accurate the description, the larger the positive number.
Similarly, the less accurate the description, the larger the negative number chosen. Ratings range from +3 to -3, very accurate to very inaccurate.
Like the semantic differential, Stapel scales produce interval data.
What is the Stapel Scale?
The Stapel Scale is a unipolar rating scale, close-ended with a single adjective, designed to measure a respondent’s attitude or perception towards a particular subject or event. It ranges from negative to positive values without a neutral point.
How is the Stapel Scale structured?
The Stapel Scale places a single adjective in the center of an even number of numerical values, such as +3 to -3 or +5 to -5. Respondents select a numerical value that best defines the validity of the adjective in relation to the subject.
Who developed the Stapel Scale?
The Stapel Scale was named after its developer, Jan Stapel.
How does the Stapel Scale differ from the Semantic Differential Scale?
While both scales produce similar interval data, the Stapel Scale is unipolar with one objective and lacks a neutral point. In contrast, the Semantic Differential Scale is bipolar, based on two opposing adjectives, and often includes a neutral option.
What are the advantages of using the Stapel Scale?
The Stapel Scale is easy to understand and respond to, uses numerical labels to reduce ambiguity, forces a response due to the absence of a neutral point, and simultaneously measures both the direction and intensity of attitudes.
In what scenarios is the Stapel Scale typically used?
The Stapel Scale is commonly used in customer satisfaction surveys to rate various attributes of a product or service individually, providing a comprehensive view of business performance.
How is the data from the Stapel Scale analyzed?
The data collected using the Stapel Scale is treated as interval data and can be analyzed similarly to data from the Semantic Differential Scale.